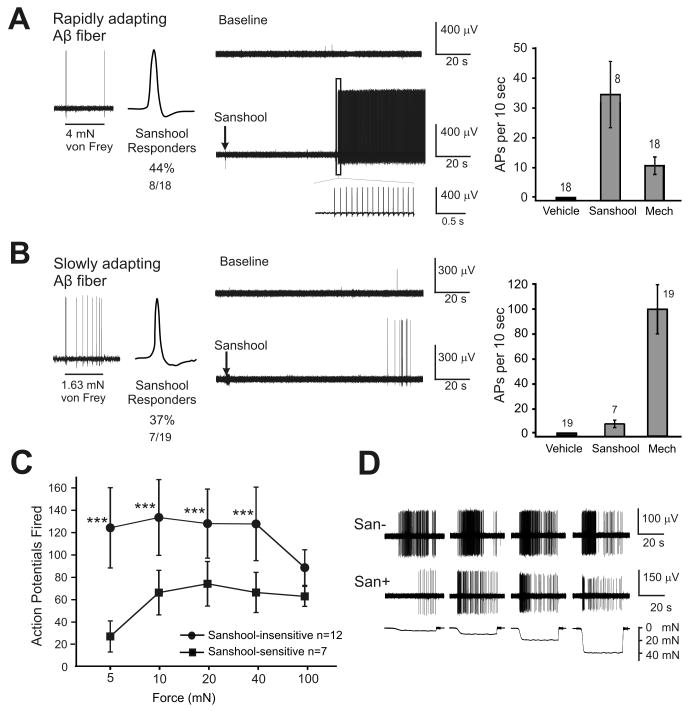
Figure 2. Sanshool activates subsets of RA and SA Aβ fibers.
Response of A) rapidly adapting Aβ and B) slowly adapting Aβ fibers to sanshool. Left: Representative response to a sustained (suprathreshold) mechanical force. Middle: Response to 200 μM hydroxy-α-sanshool. Right: Maximal firing rate in response to sanshool or mechanical stimuli (100 mN force; 10 sec). C) Number of mechanically-evoked action potentials in sanshool-sensitive and sanshool-insensitive slowly adapting Aβ fibers. Sustained force stimuli (5-100 mN; 10 sec each) were applied to each receptive field before the receptive field was exposed to sanshool. *** indicates a significant difference between the two cohorts (2-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test; p < 0.001) D) Representative examples of sanshool-sensitive and sanshool-insensitive slowly adapting Aβ fibers in response to mechanical stimuli.