Fig. 2.
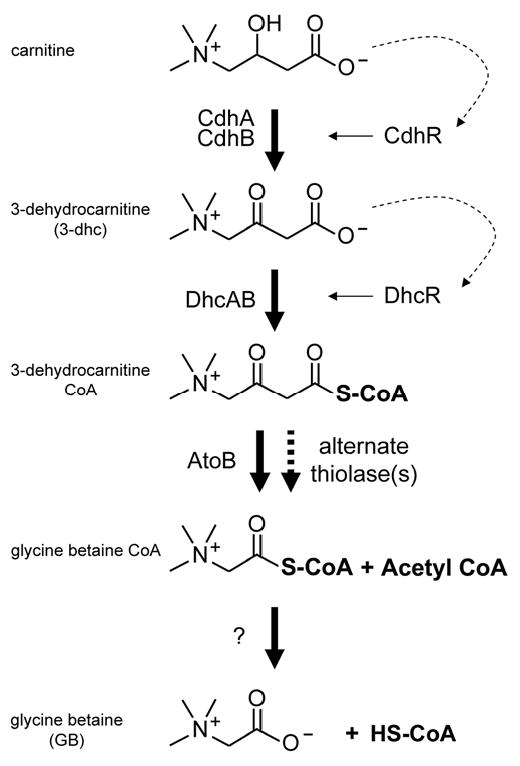
The proposed pathway for carnitine catabolism to GB in P. aeruginosa. Dashed arrows represent ligand activation of the respective transcription factor, with the solid arrows leading from the transcription factors representing transcriptional induction. Step 1: using NAD+, carnitine dehydrogenase (CDH) catalyzes the oxidation at carbon 3. Step 2: the predicted 3-ketoacid CoA-transferase encoded by dhcAB, along with a source of activated CoA, catalyzes the sulfur attack of carbon 1. Step 3: a thiolase, possibly encoded by atoB, catalyzes the deacetlyation reaction. Step 4: an unknown enzyme catalyzes the removal of CoA, leaving glycine betaine.
