Figure 3.
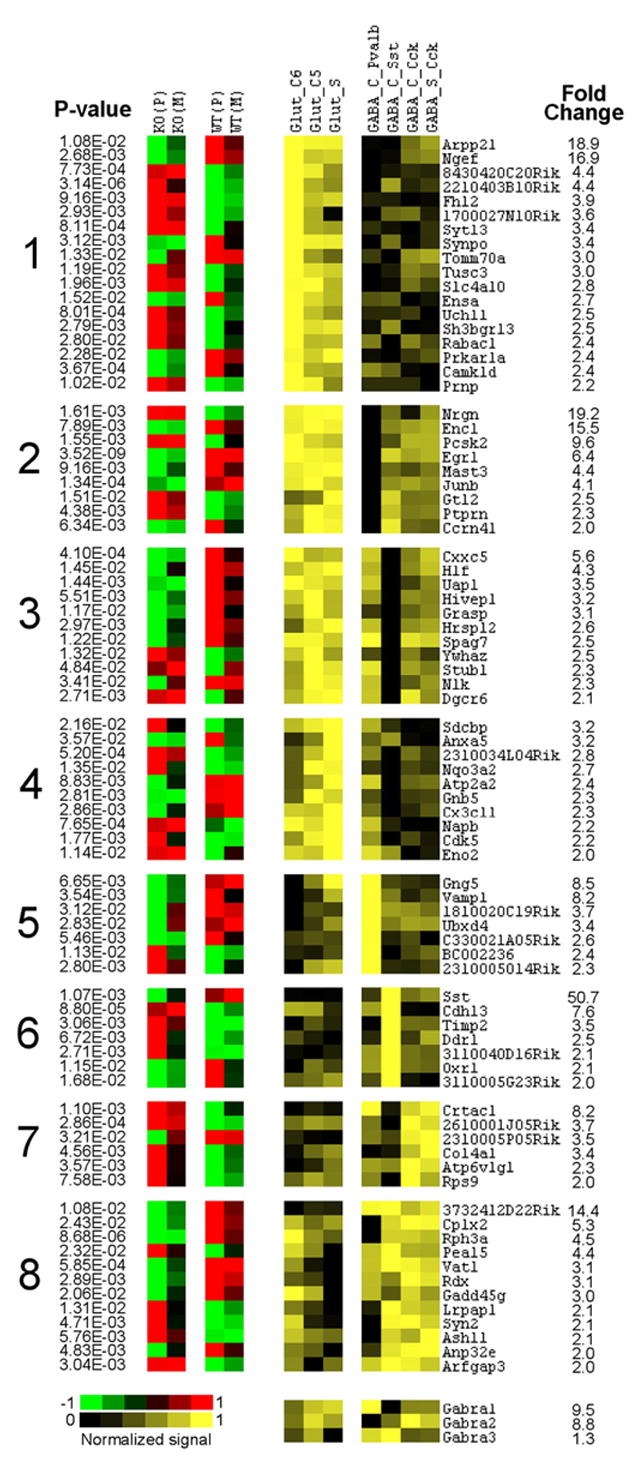
Left, Cortex-specific genes differentially expressed between knock-out (KO) and wild-type (WT) (t test; p values are shown on the left), which also show heterogeneous expression across seven types of cortical neurons (≥2-fold difference). Right, Corresponding data from MNED (Sugino et al., 2006). Fold change refers to the difference between lowest (black) and highest (bright yellow) expressing neurons. These genes are clustered according to their differential expression among three excitatory (Glut) and four inhibitory (GABA) neuronal types (for detailed description of neuronal types, see Sugino et al., 2006). The first four clusters represent genes enriched in all Glut populations but with different expression in GABA neurons. Clusters 5– 8 represent genes enriched in individual classes of GABA interneurons. Expression of three GABAA subunits across the seven neuronal populations is shown at the bottom.
