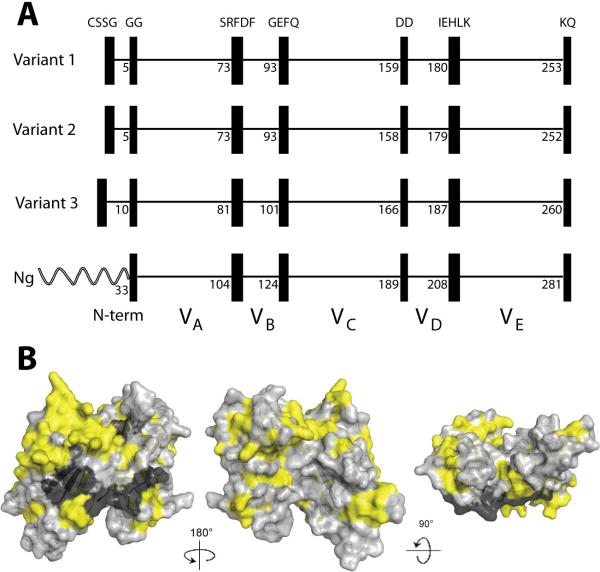
Figure 2.
Panel A. Schematic representation of fHbp showing positions of blocks of invariant residues (shown as black vertical rectangles). The top three panels show representative architectures of three N. meningitidis fHbp variants in groups 1, 2 and 3 (peptide ID numbers, 1, 16 and 28, respectively). The amino acid positions of the last residue in each variable segment are shown. With the exception of a longer, unrelated amino-terminal element, two N. gonorrhoeae orthologs (Ng, Genbank accession numbers AE004969 and CP001050) had the identical six invariant blocks of residues that flanked segments VA through VE. Panel B. Space-filling structural models of factor H binding protein based on the coordinates of fHbp in a complex with a fragment of human factor H (Schneider et al., 2009). The light gray residues represent the variable amino acids located within the modular variable segments. The invariant blocks of residues separating each of the variable segments are shown in black. The yellow residues represent the invariant amino acids outside of these blocks. The model on the left is the surface predicted to be anchored to the cell wall. The model in the center has been rotated 180 degrees on the Y-axis from the corresponding model on the left, while the model on the right has been rotated 90 degrees on the X-axis as compared with the model in the middle. The figure was constructed with PyMol (http://www.pymol.org).