Figure 1.
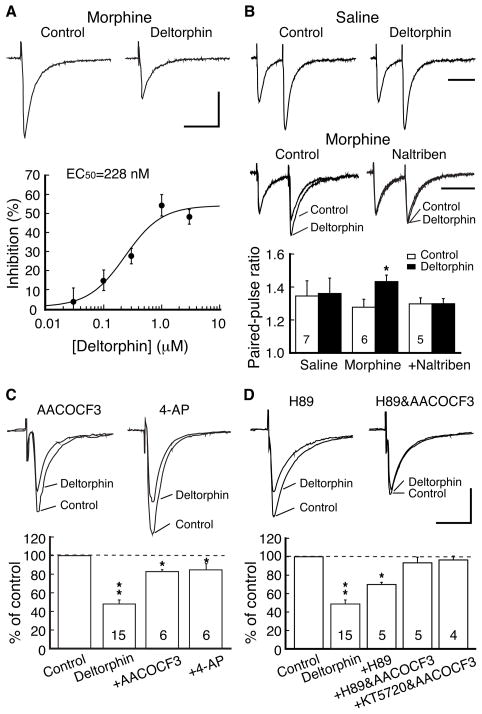
Chronic morphine-induced inhibition of GABA synaptic currents by delta-opioid-receptors (DOR) involves both the PLA2 and cAMP/PKA pathways. A, Representative GABA IPSCs (upper) before (control) and during application of the DOR agonist deltorphin (1 μM) in a brainstem neuron of the nucleus raphe magnus (NRM) from a morphine-treated rat. Also shown (lower) is a dose-response curve for the deltorphin inhibition (n=6–7 cells for each data point). Data points were fitted by a logistic function to determine the EC50 value. B, Representative IPSC pairs (upper) and summarized group data (lower) in neurons from saline-treated rats and from morphine-treated rats without and with addition of the DOR antagonist naltriben (10 μM), showing the effects of deltorphin on the paired-pulse ratio (PPR). The numbers in columns denotes cell numbers for that group. C, Deltorphin effects on GABA IPSCs in neurons of the morphine group in the presence of the PLA2 inhibitor AACOCF3 (10 μM) or the presynaptic potassium channel blocker 4-AP (100μM). D, Deltorphin effects on IPSCs in the morphine group in the presence of the PKA inhibitor H89 (1 μM) or in combination of H89 and AACOCF3 or another PKA inhibitor KT5720 (1 μM) and AACOCF3. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. Scale bars are 100 pA and 50 ms in A, C, D and 100 ms in B.