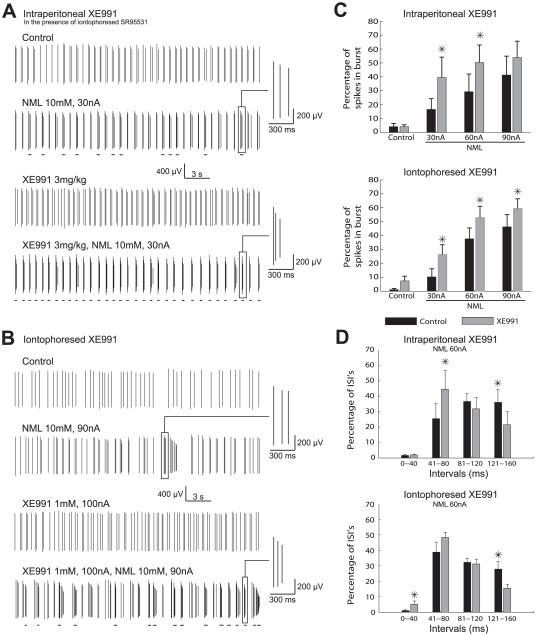
Fig. 1.
XE991 selectively enhances burst firing of DA neurons in vivo and increases the proportion of short ISIs in bursts. (A) M-current blockade was induced by a systemic administration of XE991 (3 mg/kg, i.p.). A GABAA antagonist (SR95531) was also iontophoresed (1 mm, 100 nA) during these recordings to block the most important inhibitory afferences. (B) Local M-channel blockade was performed by iontophoresis of XE991 (1 mm, 100 nA). Events that are underlined correspond to bursts (see Materials and methods for our criteria). (C) Histogram showing a significant potentiation of bursting of DA neurons during M-current blockade (intraperitoneal XE991, n = 6; iontophoresed XE991, n = 8). (D) Both intraperitoneal and local XE991 applications induced a significant shift of ISIs toward the shorter intervals, as also illustrated by the insets in (A) and (B). *P < 0.05.