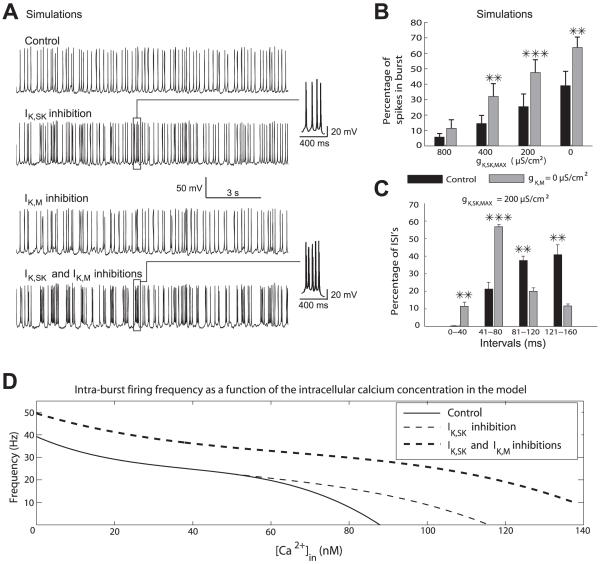
Fig. 3.
Simulations of M-current blockade on a DA neuron model confirm its selective effects on burst firing. (A) Example of a simulation. M-current inhibition was modeled by setting the M-current conductance to 0, whereas the effect of NML was modeled by reducing the IK,SK conductance (in this case to 0). The temporal pattern of synaptic inputs was exactly the same in the four traces. (B) Simulations (n = 6) showed a significant potentiation of bursting of the model DA neuron during M-current inhibition. (C) A significant shift of ISIs toward the shorter intervals is seen in the model, as also illustrated by the insets in (A). (D) Effect of IK,SK and combined IK,SK and IK,M inhibitions on the relationship between [Ca2+]in and intraburst firing rate. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.