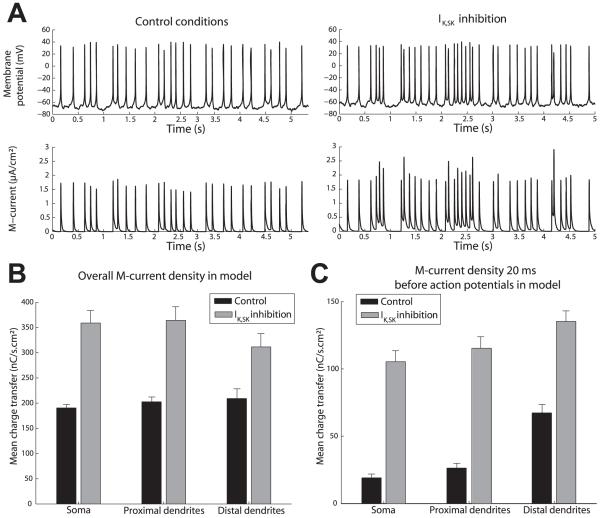
Fig. 4.
Charge transfer through M-channels in the model when SK-channels are present or absent. (A) Values of the membrane potential (top) and the amplitude of the M-current (bottom) in control conditions (left) and during a IK,SK inhibition (right). (B) Overall M-current density in model. (C) M-current density at 20 ms before action potentials in the model (n > 200 events in six modeled cells). The overall M-current density during IK,SK inhibition is only twice that in control conditions. However, the amount of M-current that opposes the generation of action potentials is much larger during IK,SK inhibition. P < 0.001 between control and IK,SK inhibition. Student’s t-test for paired values (B) and Student’s t-test for unpaired values (C).