Figure 5. The CD40 TRAF2 binding motif but not the TRAF6 binding motif is required for T-dependent germinal center responses.
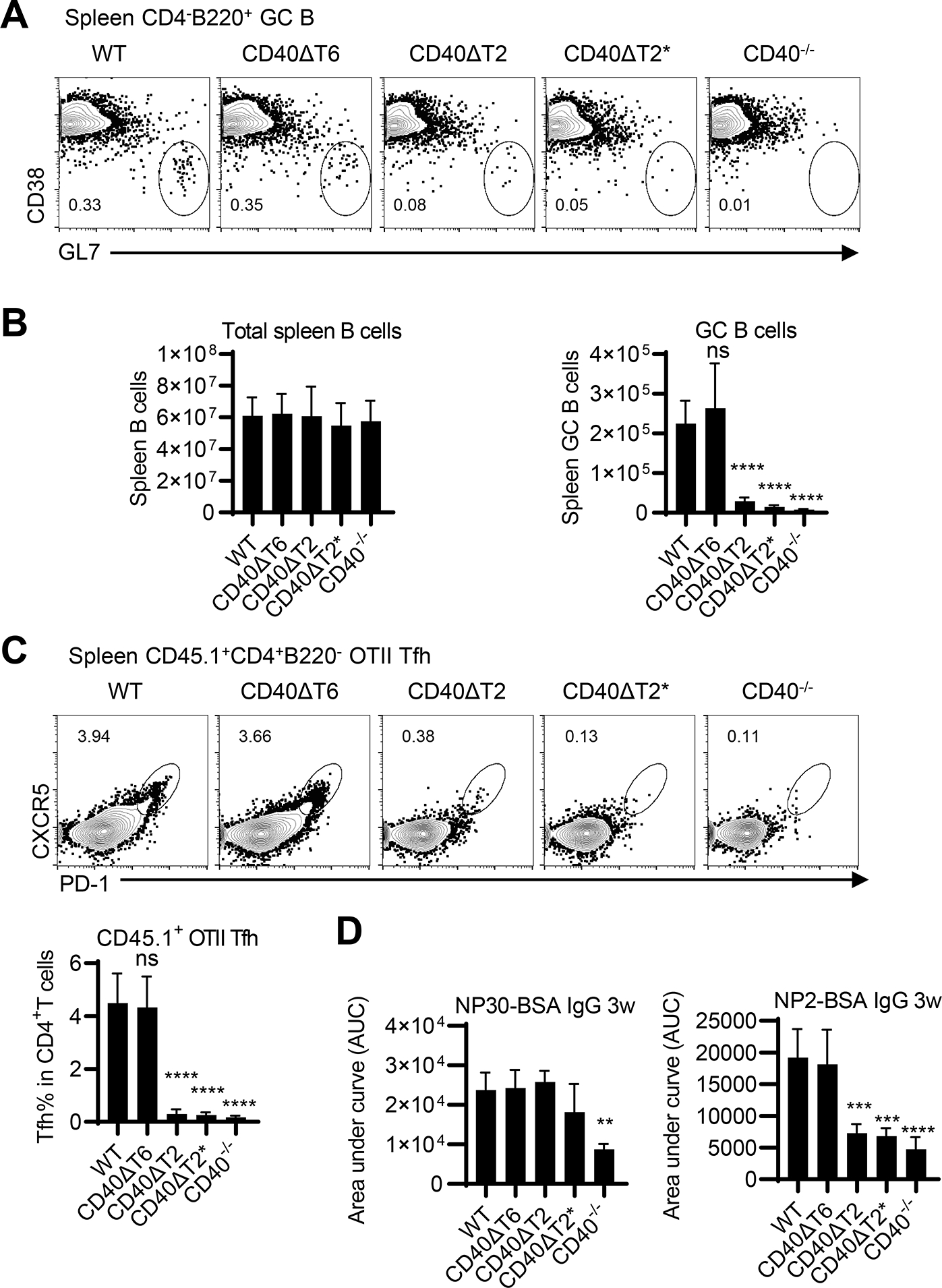
WT and CD40 mutant mice were immunized with NP-KLH in alum. After 8 days, GC B cells and total B cells were analyzed in the spleen. Representative FACS analysis (A) of CD38−GL7+ GC B cells in the CD4− B220+ B cell gate and statistical analyses of FACS data examining the total number of spleen B cells and GC B cells in each mouse strain (B). C. OT-II T cells (CD45.1) were transferred to the indicated recipient mice (CD45.2) and were immunized with NP-OVA/alum one day after cell injection. Transferred OT-II cells were analyzed at day 8 by FACS analysis. A representative flow cytometry profile of spleen OT-II cells (CD45.1+CD4+B220−) analyzed for the Tfh CXCR5high PD-1high phenotype and statistical analyses of FACS data showing the percentage of transferred OT-II cells expressing a Tfh phenotype were shown. D. WT and CD40 mutant mice were immunized with NP-KLH in alum. Serum was collected three weeks after immunization, and total NP-specific antibody (anti-NP30 IgG) and high-affinity NP antibody (anti-NP2 IgG) was determined by ELISA. Data are combined from two independent experiments (mean ± S.D. using 6 mice per group). One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test against immunized WT group was performed for multiple comparisons. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001.
