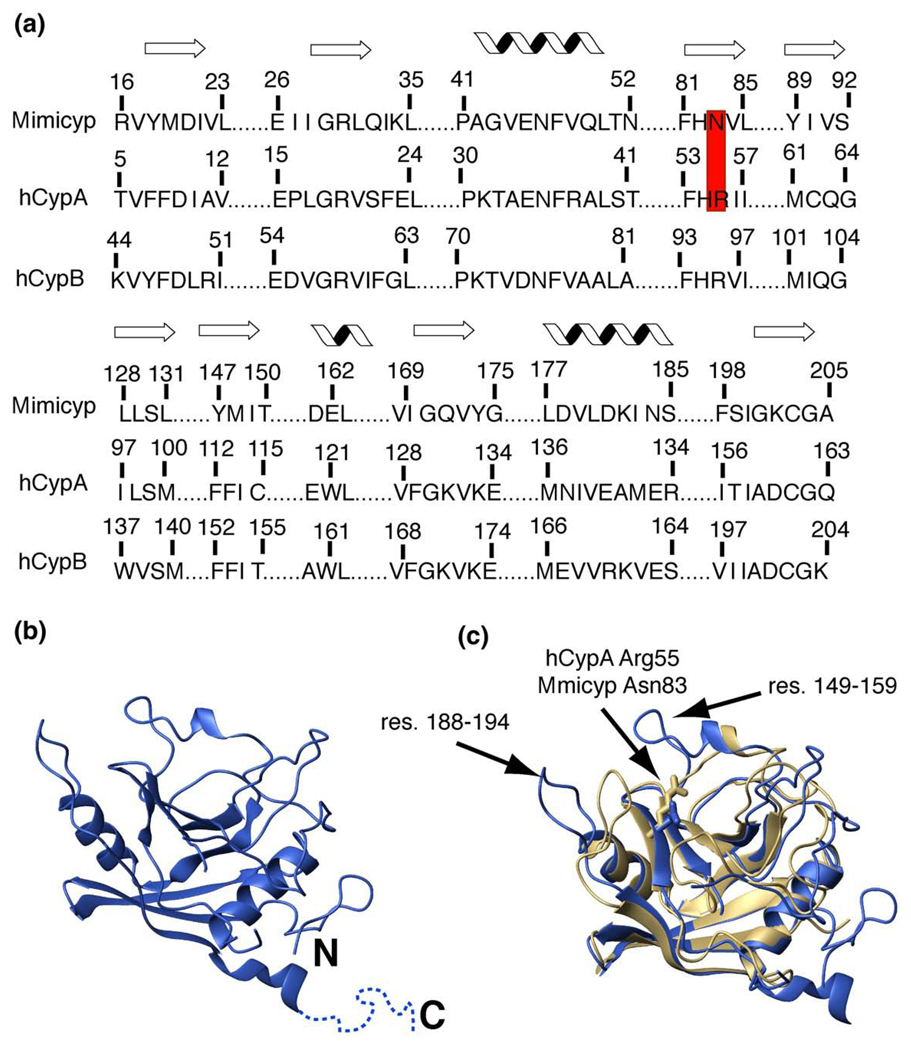
Figure 1.
Mimicyp sequence and structural comparison to hCypA. (a) The sequence alignment of the secondary structural elements for mimicyp and hCypA with the secondary structure (either β-strand or α-helix) shown above. In mimicyp, Asn83 replaces the catalytic residue in hCypA, Arg55 (red). (b) The X-ray crystal structure of monomeric mimicyp is shown (blue). The C-terminal residues 214–234 that do not give rise to observable density are shown as dotted lines. (c) Overlay of mimicyp (blue) with hCypA (gold) using all backbone nuclei of secondary structure elements (74 residues within each protein) results in an RMSD of 1.02 Å. The conserved catalytic Arg55 of hCypA and non-conserved Asn83 of mimicyp are shown for a comparison. Residues 149–158 that are not present in hCypA and residues 188–194 that deviate from hCypA are designated with arrows.