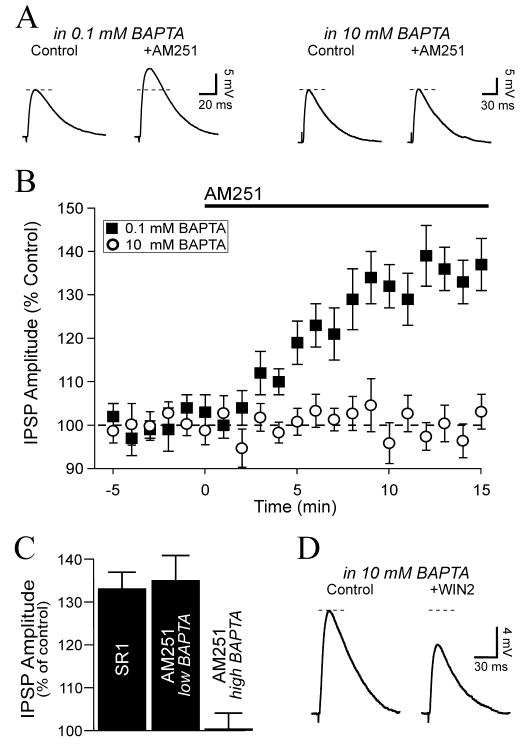
Figure 5. Intracellular calcium buffering with BAPTA eliminates tonic CB1 activity.
A. Whole-cell recordings from CeA neurons using patch pipettes containing BAPTA at low (0.1 mM, control condition) or high (10 mM, to buffer intracellular calcium) concentrations. The CB1 antagonist AM251 (2 μM) increased the IPSP by 45% when the intracellular recording solution contained low BAPTA (left; RMP was -71 mV), whereas a recording solution containing high BAPTA (right; RMP was -73 mV) prevented the effect of AM251. Dotted line is control amplitude. B. Average time course of the effect of 2 μM AM251 on inhibitory transmission in neurons recorded with pipettes containing low or high BAPTA. C. On average, the effect of SR1 on IPSPs was comparable to the effect of AM251 in neurons recorded in low BAPTA, whereas in neurons loaded with high BAPTA the effect of AM251 on IPSPs was completely prevented. D. The inclusion of high BAPTA in the recording pipette did not prevent the WIN2-elicited decrease of inhibitory transmission (RMP was -69 mV).