Table 1.
Highest-Ranking Hits Emerging from Virtual Screening of a Leadlikea Library of ~1 Million Compounds to the Reactiveb (That Is, Transition State) Form of GR Versus the Outcome of Experimental GR Assays
| Compound | Predicted Interaction Energy (kcal/mol) from docked poses | Predicted pKi from docked posesc | Experimental Resultsd |
|---|---|---|---|
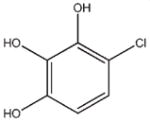 1 |
−21.996 | 10.1 | Colloidal Aggregatee |
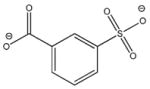 2 |
−25.897 | 10.1 | IC50 = 3.0 mM |
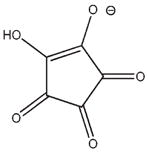 3g |
−13.530 | 9.9 | Ki = 42 ± 10 μM |
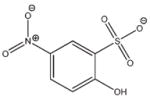 4 |
−20.511 | 9.5 | IC50 = > 2.4 mMf |
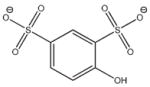 5 |
−12.156 | 9.1 | Ki = 59 ± 13 μM |
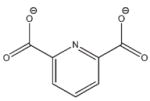 6h |
−23.950 | 8.3 | Ki = 1.9 mM |
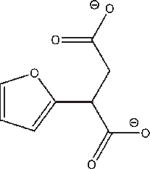 7h |
−25.015 | 7.2 | IC50 = 3.5 mM |
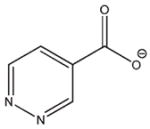 8 |
−14.367 | 6.6 | IC50 = 4.0 mM |
The Chemical Computing Group Conformational Database Version 2007, where lead-likeness is based on Oprea’s parameters;14 see Computational Procedures in the Supporting Information.
The reactive form of GR, as characterized by Spies et al.9
As determined by the London dG scoring function, implemented within the LigX utility of MOE (v2008.10);15 values above pKi=9.0 were considered for experimental investigation.
All Ki or IC50 values determined by the circular dichroism assay are described in the Supporting Information, except for 1 and 4.
Compound 1 appeared to display noncompetitive inhibition with an apparent Ki=90 ± 7 μM but was found to inhibit GR through colloidal aggregation.
Inhibition by 4 was measured using the coupled enzyme assay, and the actual IC50 is expected to be higher due to partial inhibition of the coupled enzyme, L-glutamate dehydrogenase (see the Supporting Information for details).
Compounds 6 and 7 were chosen for their high interaction energies, while 8 was a readily available fragment of 2, 4, 5, and 6.
