Figure 8.
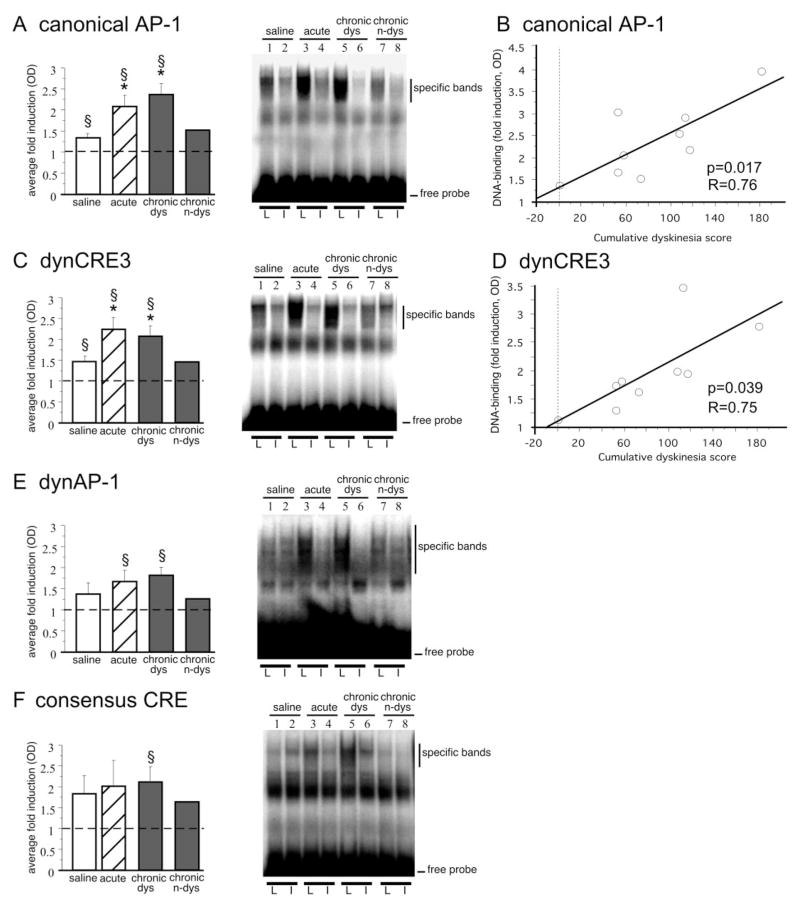
Acute and chronic treatment with L-DOPA induces striatal DNA binding activity to the canonical AP-1 (A), the dynCRE3 (C), the dynAP-1 (E), and the consensus CRE (F). Optical densities of specific bands are expressed as the fold induction on the lesioned over the intact side. *p < 0.05 versus saline group; §p < 0.05 versus intact side; values give means + SEM; n ≥ 5 in all groups but chronic n-dys (i.e., chronically L-DOPA-treated but nondyskinetic case). As shown in B and D, only one animal remained nondyskinetic (0 cumulative dyskinesia scores) during chronic L-DOPA treatment. In B and D, levels of binding to the canonical AP-1 (B) and dynCRE3 (D) in the chronic L-DOPA cases are plotted on the cumulative axial, limb, and orolingual AIM scores recorded from the same animals. The probability value (p) and correlation coefficient (R) of the corresponding simple regression equation are given in the bottom right corner. L, 6-OHDA-lesioned side; I, contralateral intact side.