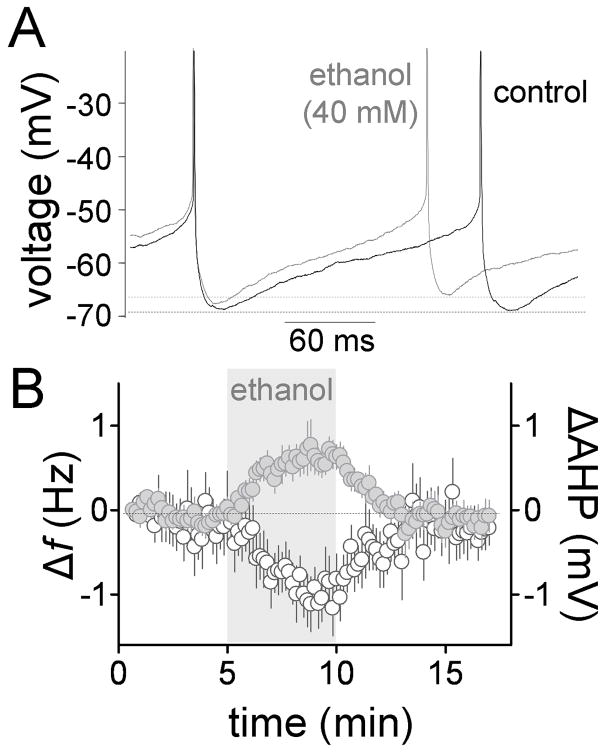
Fig 3. Ethanol increases spontaneous firing and decreases AHP amplitude in the perforated-patch configuration.
A, representative trace illustrating that ethanol increases f and slightly decreases the AHP (action potentials were truncated for clarity). B, time course of the ethanol-induced Δf (gray circles) and ΔAHP (AHP peak amplitude change; white circles) (n = 8). Recordings were obtained in presence of gabazine (10 μM), kynurenate (1 mM), D,L-APV (50 μM), strychnine (1 μM), CGP 54626 (10 μM), and LY 341495 (1 μM).