Figure 2.
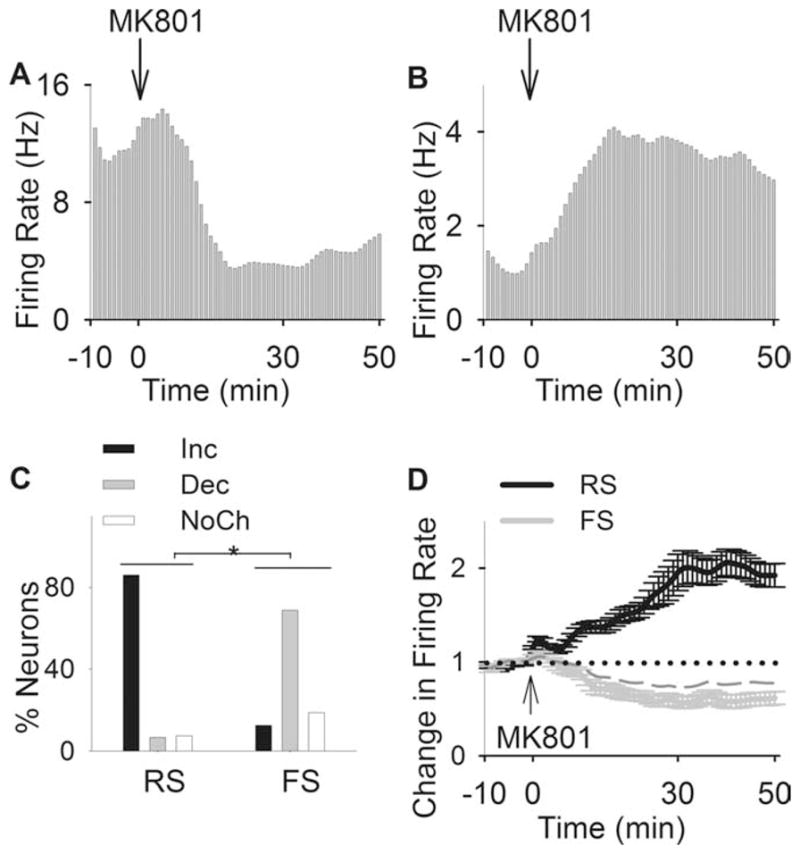
Inhibitory effects of MK801 on putative interneurons. A, B, Examples of inhibitory and excitatory effects of MK801 on an individual interneuron (A) and a pyramidal neuron (B). Each panel depicts the firing rate histogram (bin, 1 min; smoothed with a Gaussian filter with bin width of 3) of a single unit. Arrow indicates the time of MK801 injection. C, Distribution of firing rate responses (increase, decrease, or no change) to MK801 was significantly different among populations of RS and FS units (*p < 0.001). D, Comparison of average population response of RS and FS units to MK801. Two-way ANOVA with time as the repeated measure revealed a significant effect for neuron type (F(1,259) = 12.96; p <0.001), time (F(59,15281) = 2.71; p <0.001), and type by time interaction (F(59,15281) = 5.94; p < 0.001). The averages for all FS units and those with a decreased response type have been depicted as dashed and solid gray lines, respectively.
