Figure 6.
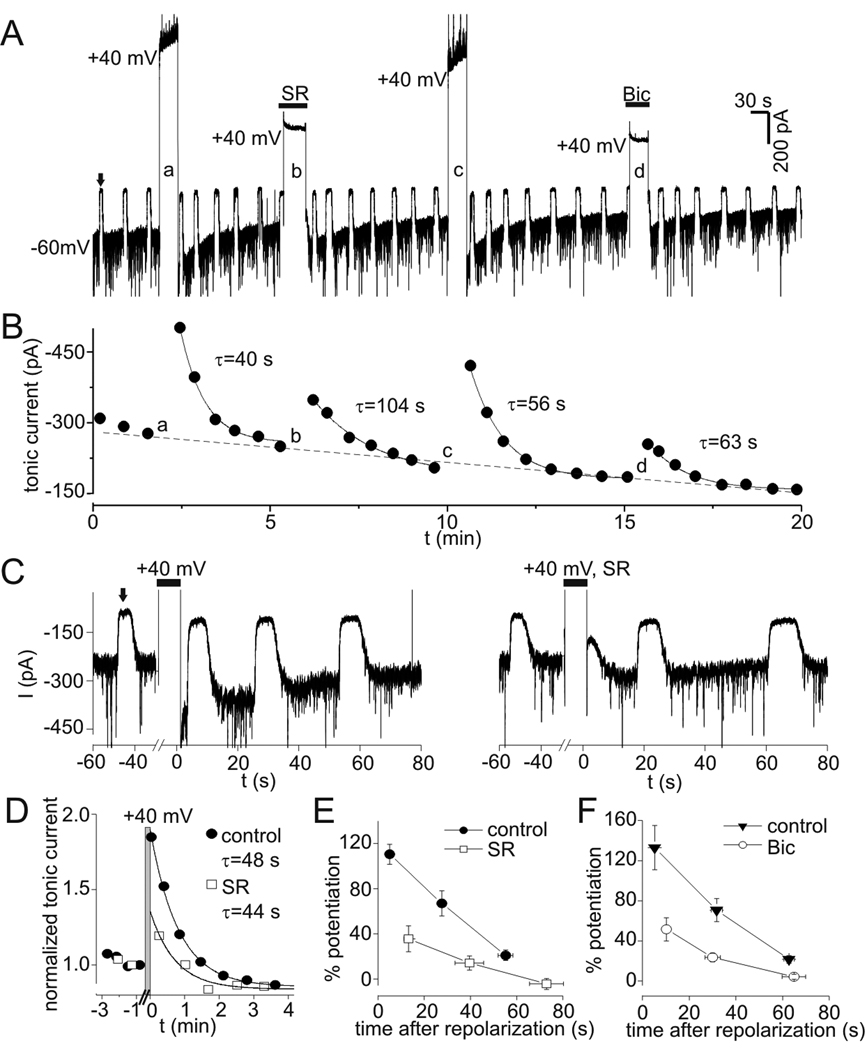
PDP of tonic currents. A: Tonic currents in the presence of low levels of exogenous GABA (0.3 µM). Upward deflections (e.g. the one indicated by solid arrow) represent response to 10 µM bicuculline (Bic) used to measure tonic current amplitude. Tonic current at −60 mV was increased by transient depolarization to +40 mV (large upward deflections). This increase was attenuated when depolarization occurred in the presence of the GABAA receptor antagonists SR95531 (SR, 100 µM) or Bic (10 µM). B: Tonic current amplitude from experiment in panel A. Solid lines represent single exponential fits, time constants (τ) for recovery after each depolarization are indicated. Lower case letters refer to sequentially labeled depolarizations in panel A. Note the progressive rundown of tonic current over duration of experiment (dashed line), which was seen in 11/11 cells studied with 0.3 µM GABA. C: PDP of tonic currents under control conditions (left panel) and when depolarization occurred in the presence of SR (right panel) on expanded time scale (different neuron than in A–B). Wash off of SR occurred in <10 s and was complete prior to measuring tonic current with Bic. D: Normalized tonic current from data in C. Data was normalized to value immediately preceding each depolarization and aligned so that repolarization occurred at t=0. Gray bar indicates period of depolarization to +40 mV. PDP in the presence of SR is reduced compared to control for 1 min after repolarization, much longer than the time required for wash of SR. Solid lines are single exponential fits to data with indicated time constants. E: Potentiation of first three measurements of tonic current after repolarization for experiments with and without SR. Peak PDP with SR was significantly reduced compared to both the first and second measurements under control conditions (p<0.01, n=5). F: Potentiation of tonic current vs. time after repolarization for experiments with and without Bic. PDP induced in Bic was significantly reduced compared to each corresponding control measurement (p<0.01, n=6).
