Figure 8.
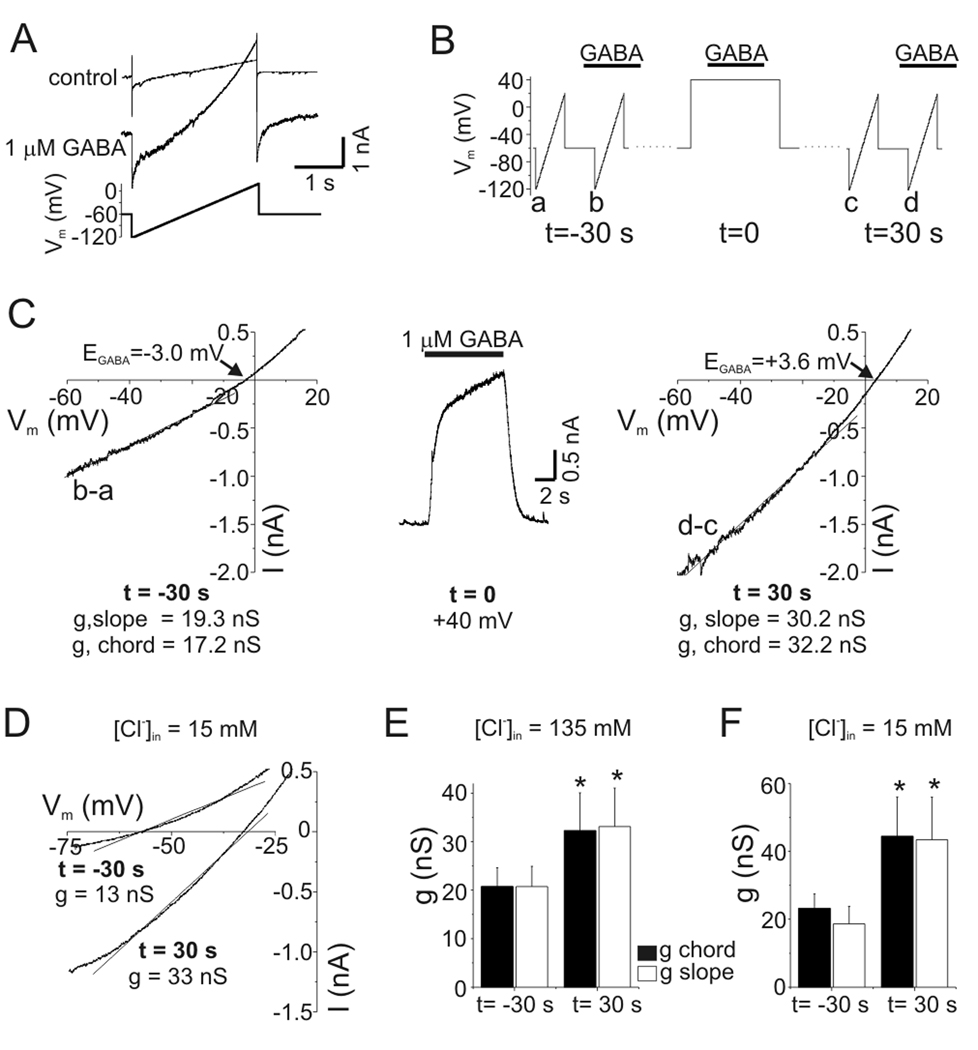
PDP of GABA current was due to increased conductance. A: Membrane currents in response to voltage ramps before (control) and after GABA application (1 µM). The GABA-evoked ramp current (“difference current”) was obtained from point-by-point subtraction of these data for determination of reversal potential (i.e. EGABA) and slope conductance. B: Schematic of experimental protocol. Difference currents were obtained with voltage ramps 30 s before (t =−30 s) GABA was applied to a neuron depolarized to +40 mV (t=0) and then 30 s after this depolarization (t=30 s). C: GABA-evoked ramp currents during PDP. Difference currents are plotted as a function of voltage in the left- (t=−30 s) and right-hand (t=30 s) panels. Middle panel shows GABA response at +40 mV (t=0). Slope conductance was determined from a linear fit to current between −60 and −10 mV (solid lines in left-hand and right-hand panels). Chord conductance was calculated using the measured EGABA (indicated in figure) and current at −60 mV. Voltage ramps were given ~2 s into GABA applications. Slope and chord conductance were both increased by depolarization (values in figure). D: GABA-evoked (3 µM) ramp currents from a neuron recorded with pipette solution containing 15 mM Cl−. Same protocol as B-C. EGABA shifted from −57 mV at baseline (t=−30 s) to −32 mV after depolarization (t=30 s). Slope conductances are indicated in figure. E: Mean values of slope and chord conductance for experiments with [Cl−]in = 135 mM. The slope and chord conductances were increased by 60% and 56%, respectively (n=5, p<0.05). Legend applies to this panel and panel F. Data with [Cl−]in = 135 mM were pooled from experiments with 1–3 µM GABA. F: Mean values of slope and chord conductance for experiments with [Cl−]in = 15 mM. During PDP with [Cl−]in = 15 mM, conductance was increased by 91–132% (n=5, p<0.05). Data with [Cl−]in = 15 mM were obtained with 3 µM GABA.