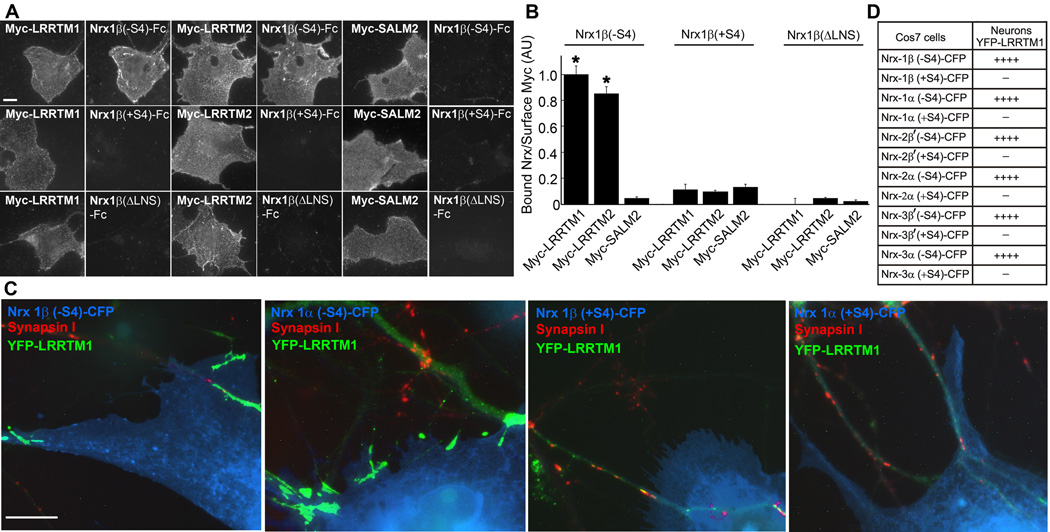
Figure 4. LRRTM1, the Family Member Linked to Schizophrenia, Also Binds and Is Recruited by (−S4) Neurexins.
A. Recombinant Nrx1β(−S4)-Fc, Nrx1β(+S4)-Fc and Nrx1β(ΔLNS)-Fc were incubated with COS7 cells transfected with Myc-LRRTM1, Myc-LRRTM2 or Myc-SALM2. Both Myc-LRRTM1 and Myc-LRRTM2, detected by surface staining for Myc, bound Nrx1β(−S4)-Fc but not Nrx1β(+S4)-Fc or Nrx1β(ΔLNS)-Fc. Myc-SALM2 was the negative control for binding. Scale bar, 10 µm.
B. Quantitation of the data in panel A (ANOVA, p<0.0001, posthoc Tukey’s test *p<0.001 in comparison to Myc-SALM2, n=20, results are expressed as mean ± SEM).
C. Hemi-synaptogenesis assay as described in Figure 3. COS7 cells expressing Nrx1β(−S4)-CFP or Nrx1α(−S4)-CFP but not Nrx1β(+S4)-CFP or Nrx1α(+S4)-CFP clustered YFP-LRRTM1 expressed in neurons. Scale bar, 10 µm.
D. The assay in panel C was also performed for +S4 and −S4 variants of neurexins 2β', 3β', 2α and 3α. All (−S4) neurexin variants clustered YFP-LRRTM1 expressed in neurons. These clusters contained PSD-95 but not synapsin. (++++ 80–95% contact sites were positive. −0–5% contact sites were positive, n>30 contact sites).