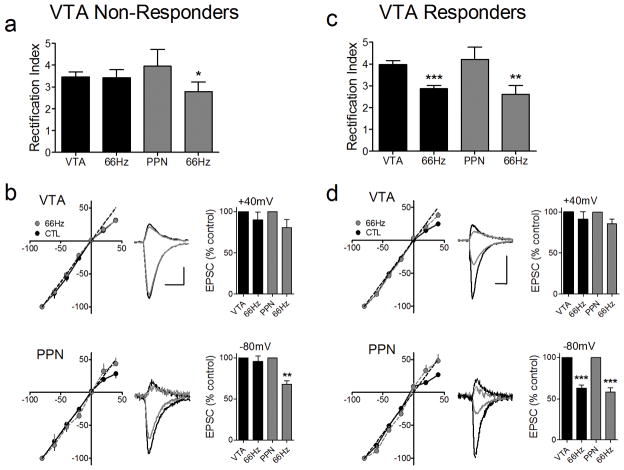
Figure 5.
A single injection of Δ9-THC leads to a pathway specific change in the subunit composition of synaptic AMPAR. (a) The RI of intra-VTA-activated EPSCS is not altered by 66Hz stimulation following Δ9-THC administration, in a subset of VTA DA neurons (VTA Non-Responders, 9/20 cells). However, in the same cells, the RI of all PPN-activated EPSCs was significantly decreased following 66Hz induced LTD. (b) EPSC I-V curves from the PPN and intra-VTA glutamate pathways before and after 66Hz stimulation (scale bars = 5 ms, 200 pA for VTA examples; 5 ms. 100 pA for PPN examples). (c) In another group of cells (VTA Responders, 11/20), both the VTA and PPN undergo significant changes in the RI following 66Hz stimulation. (d) EPSC I-V curves in both the PPN and VTA pathways before and after 66Hz stimulation. Note that both pathways exhibit linear I-V curves after 66Hz induced LTD. Scale bars are 5 ms and 200 pA for the VTA examples and 5 ms and 100 pA for the PPN examples.