Figure 1.
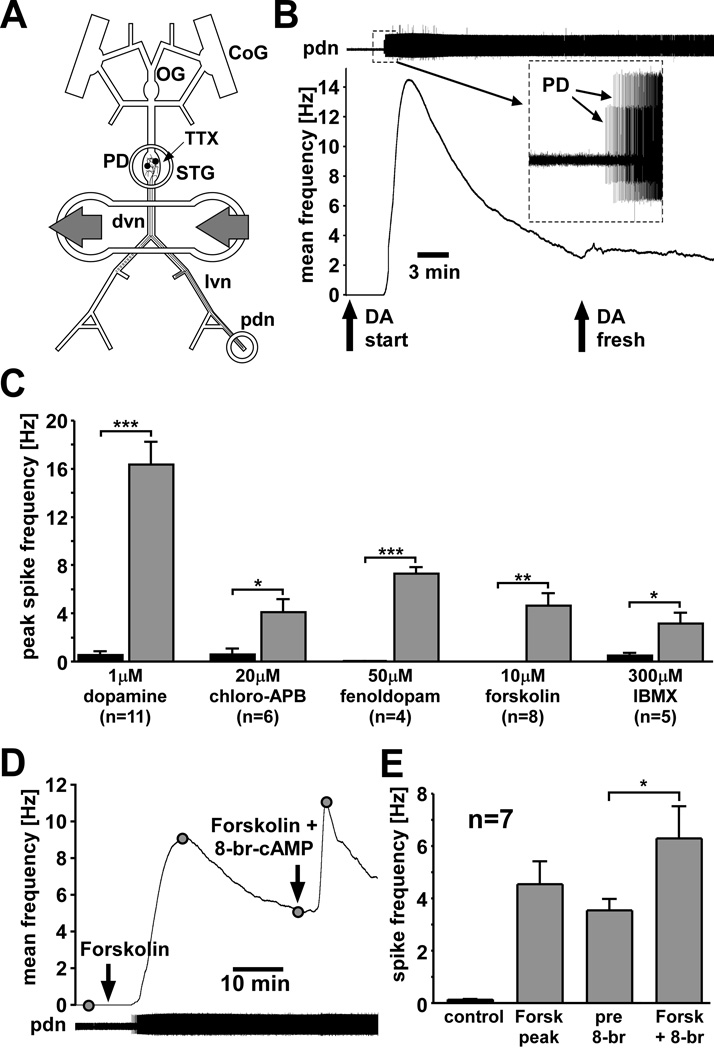
Peripheral spike initiation by DA and drugs that increase cAMP levels. A: Experimental preparation. Centrally generated activity was blocked by application of 100 nM TTX in saline to the STG. Pharmacological agents were applied to a petroleum jelly well built around a part of the dvn and proximal lvns. Extracellular recordings of PD neuron activity were obtained from a well built around the pdn. B: PD axon response to application of 1 µM DA. The upper trace shows an extracellular record with different amplitude spikes from both PD neurons (inset). Spiking started after DA application. The plot of mean spike frequency over time (bin size: 30 s) shows a fast peak and substantial slow decay of frequency. Spike frequency is not changed by application of fresh DA. C: Peak spike frequencies across experiments compared between control and different drugs. Significance was tested with paired t-tests. D: Mean PD axon spike frequency (bin size: 30 s) in response to application of forskolin and subsequent application of forskolin + 8-br-cAMP. E: Mean spike frequencies in control, peak value in forskolin, and before and after application of forskolin + 8-br-cAMP. 8-br-cAMP significantly enhanced spiking (paired t-test).