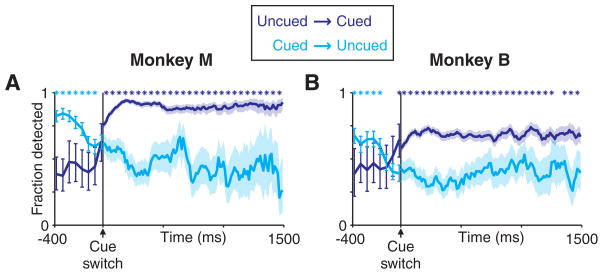
Figure 3.
Behavioral shift of attention begins for speed pulses occurring before the cue switch. Fraction of speed pulses detected for various speed-pulse times relative to the cue switch are shown for monkey M (A) and monkey B (B). For pre-cue-switch behavior, speed pulses occurred randomly at fixed times spaced four video frames (~53 ms) apart. For post-cue-switch behavior, speed pulses could occur at any video frame, but data were smoothed using a sliding window four video frames wide. Error bars and shaded regions are 95% confidence intervals for the mean. Time points with significant differences are marked by an asterisk, with the color indicating the condition with the greater detection rate (p < 0.05, χ2 test).