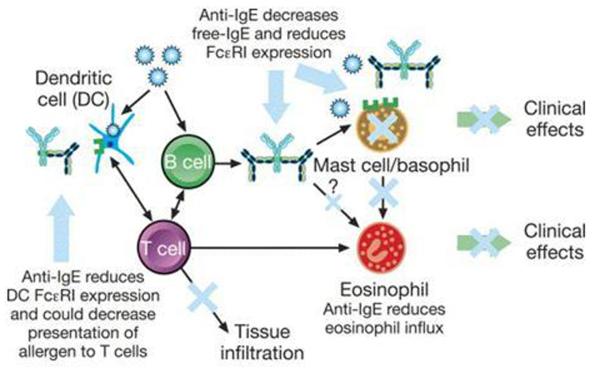
Figure 3.
Proposed mechanisms of action of omalizumab. Omalizumab decreases free IgE levels and reduces FcεRI receptor expression on mast cells and basophils. This results in decreased mast cell activation and sensitivity, leading to a reduction in eosinophil influx and activation. Anti-IgE treatment with omalizumab might result in decreased mast cell survival. Omalizumab also reduces dendritic cell FcεRI receptor expression. Reprinted from J Allergy Clin Immunolology, 115(3), Holgate, S. et al., The anti-inflammatory effects of omalizumab confirm the central role of IgE in allergic inflammation, p. 459-65, 2005, with permission from Elsevier [29]