Figure 3. Molecular response of M14 melanoma cells to vinblastine and IFN-α.
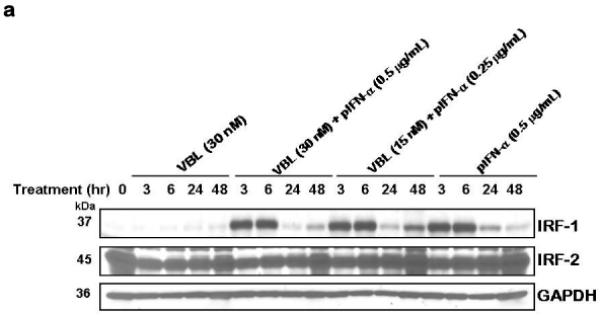
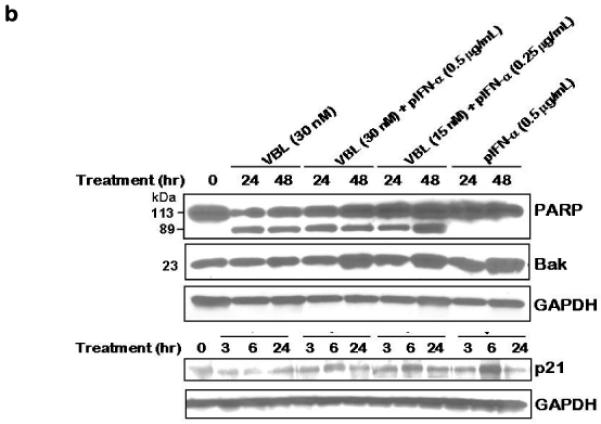
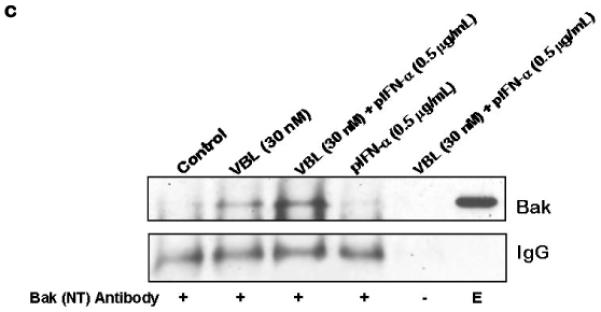

(a) IRF-1 and not IRF-2 is induced specifically in response to pegylated IFN-α in M14 melanoma cells. M14 cells were treated for the indicated time with either vinblastine (VBL), pegylated IFN-α2b (pIFN-α), or a combination of both at the indicated concentrations. Cell extracts (50 mg/lane) were immunoblotted for IRF-1 or IRF-2. Immunoblotting for GAPDH served as the loading control. (b) Induction of IRF-1 downstream targets in response to IFN-α and combined effect of IFN-α and vinblastine on PARP induced apoptosis in M14 cells. Cells were treated with the indicated drug concentrations of vinblastine or pegylated IFN-α (pIFN-α) and harvest at the given time points. Cell extracts were subjected to immunoblotting for PARP, Bak and p21. Immunoblotting for GAPDH served as the loading control. (c) Treatment of M14 cells with IFN-α and vinblastine causes induction and activation of Bak. M14 melanoma cells were untreated or treated with Vinblastine (30 nM) or pIFN-α (0.5 mg/mL) alone or in combination (30 nM Vinblastine + 0.5 pIFN-a mg/mL) for 36 h. Lysates were immuno-precipitated with anti-Bak-NT antibody for active form of Bak followed by immunoblotting for Bak. Precipitates prepared in the absence of the antibody (−) and whole cell extract (E) were also examined as controls. (d) BH3 peptide mediated cytochrome c release from mitochondria of M14 melanoma cells. Mitochondria (25 μg/reaction) isolated from M14 cells without and after treatment with 0.5 mg/ml IFN-α for 48 h were incubated with the indicated concentrations of BH3 peptide for 30 minutes at room temperature. Supernatant was collected and cytochrome c (cyt.c) release observed by immunoblotting. DMSO vehicle was 2% final in all samples.
