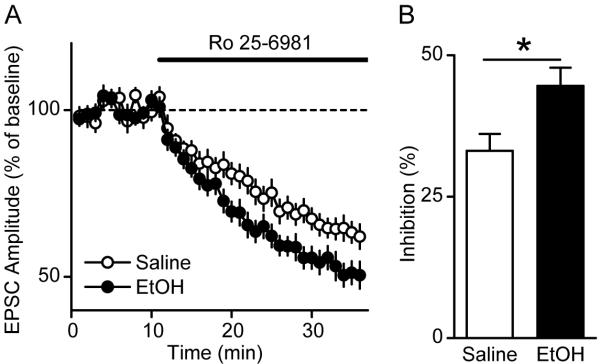
Figure 3. Repeated ethanol administration results in an increase in contribution of NR2B subunits to the activity of the channel in the DMS.
A, Time course of NMDAR EPSCs in DMS neurons from ethanol- and saline-treated rats before and during bath application of the NR2B-NMDAR-specific antagonist, Ro 25-6981 (0.25 μM) (as indicated by the horizontal line). Rats received injections of ethanol (2 g/kg, i.p.) or saline once a day for 7 days. DMS slices were prepared 16 hrs after the last injection. n = 17 (saline) and 15 (ethanol) slices. B, Summary of the mean inhibition magnitude of NMDAR-EPSCs by Ro 25-6981 in DMS neurons from saline- and ethanol-treated animals. *P < 0.05, t-test.