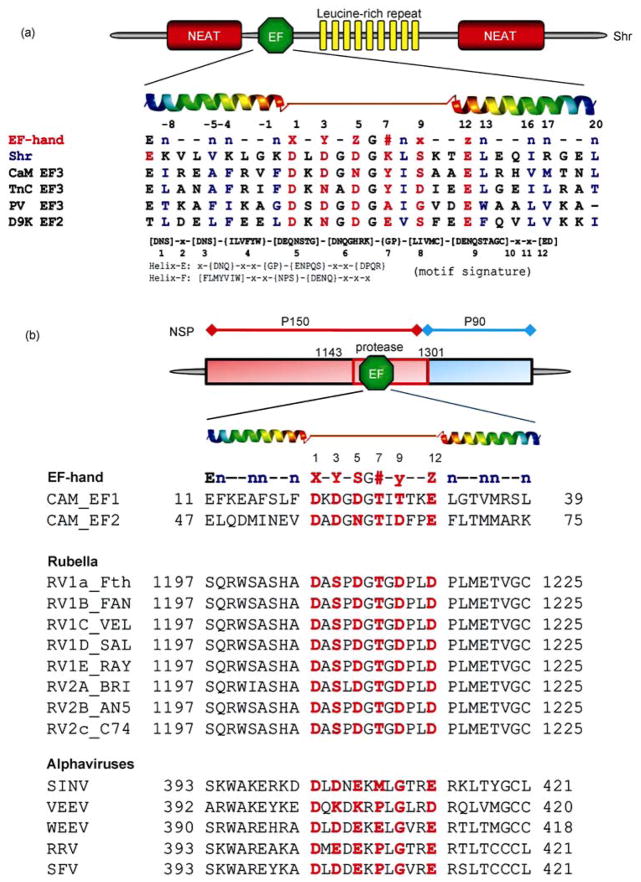
Figure 4.
Examples of predicted EF-hand Ca2+ binding motifs. (A) Predicted function domains of Shr and Tte consensus sequence of canonical EF-hand motif with coordination ligand positions (red) in the EF-hand (1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12) and the hydrophobic residues (n, blue). The predicted EF-hand from Shr (Streptococcal hemoprotein receptor, S. pyrogenes) and PlcR (phospholipase accessory protein, P. aeruginosa) are aligned with some EF-hands known to form oligomers: CaM EF3, the third EF-hand from calmodulin; TnC EF3, the third EF-hand from troponin C; PV EF3, the third EF-hand from parvalbumin; D9K EF2, the canonical EF-hand from calbindin D9K, The search patterns used for the identification of the EF-hand loop and flanking helices (Helix E and Helix F) are also shown in the bottom. (B) Predicted EF-hand motifs in Rubella and alphavirus. An EF-hand motif was predicted in the protease domain of rubella virus or the putative methyltransferase domain of nsP1 of alphaviruses. Both rubella virus and alphaviruses belong to the Togaviridae family. RV, Rubella virus; SINV, Sindbis virus; VEEV, Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus; WEEV, Western equine encephalitis virus; RRV, Ross River virus; SFV, Semliki forest virus. Adapted with permission from ref. [6, 41].