Figure 4. ERK1 KO and WT littermates develop similar mechanical hypersensitivity following peripheral nerve injury.
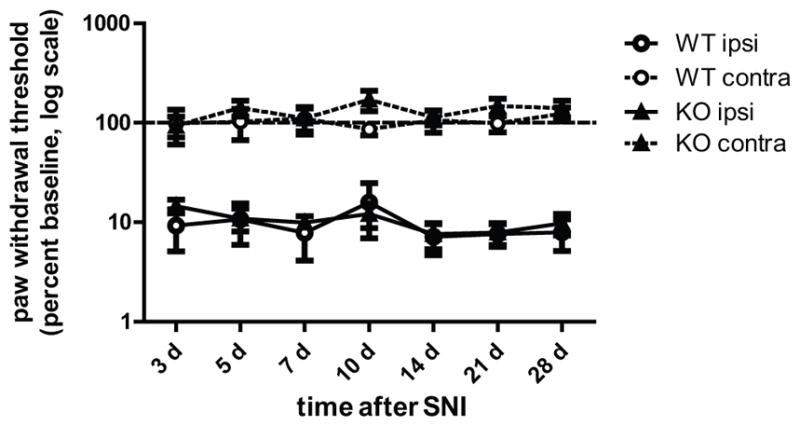
One day after baseline measurements, WT (n=9) and ERK1 KO (n=10) littermates were anesthetized and the tibial and common peroneal branches of the sciatic nerve were ligated then transected, leaving the sural branch intact. Following the spared nerve injury surgery, paw mechanical withdrawal thresholds were measured ipsilateral (solid lines) and contralateral (dashed lines) to nerve injury. Baseline and post-injury withdrawal thresholds were determined by probing the lateral plantar surface of the paw, which is innervated by the sural nerve. Data are represented as percent baseline within each subject. Error bars indicate S.E.M.
