Figure 5. ERK1 contributes to the onset of heat hypersensitivity following intraplantar formalin injection.
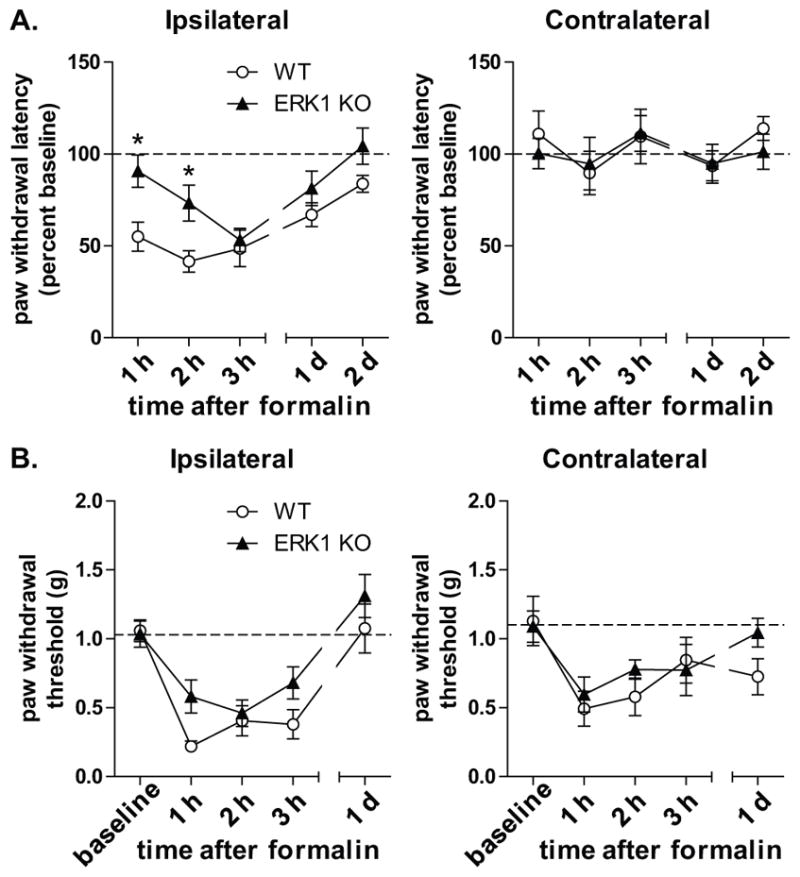
A. To assess the role of ERK1 in long-term formalin-induced heat hypersensitivity, WT (n=8) and ERK1 KO (n=8) littermates were injected with 2% formalin subcutaneously into the plantar side of the right hindpaw. Paw withdrawal latencies were measured before and after injection and are graphed as percent of pre-injection baseline. ERK1 KO mice have reduced hypersensitivity to heat at 1 and 2 h after formalin injection in the ipsilateral paw (2-way RM ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test; *p<0.05). B. To measure formalin-induced mechanical hypersensitivity, WT (n=8) and ERK1 KO (n=9) littermates were injected with 3.5% formalin. Paw withdrawal thresholds were obtained using von Frey filaments. There were no statistically significant differences between WT and ERK1 KO. Error bars reflect S.E.M.
