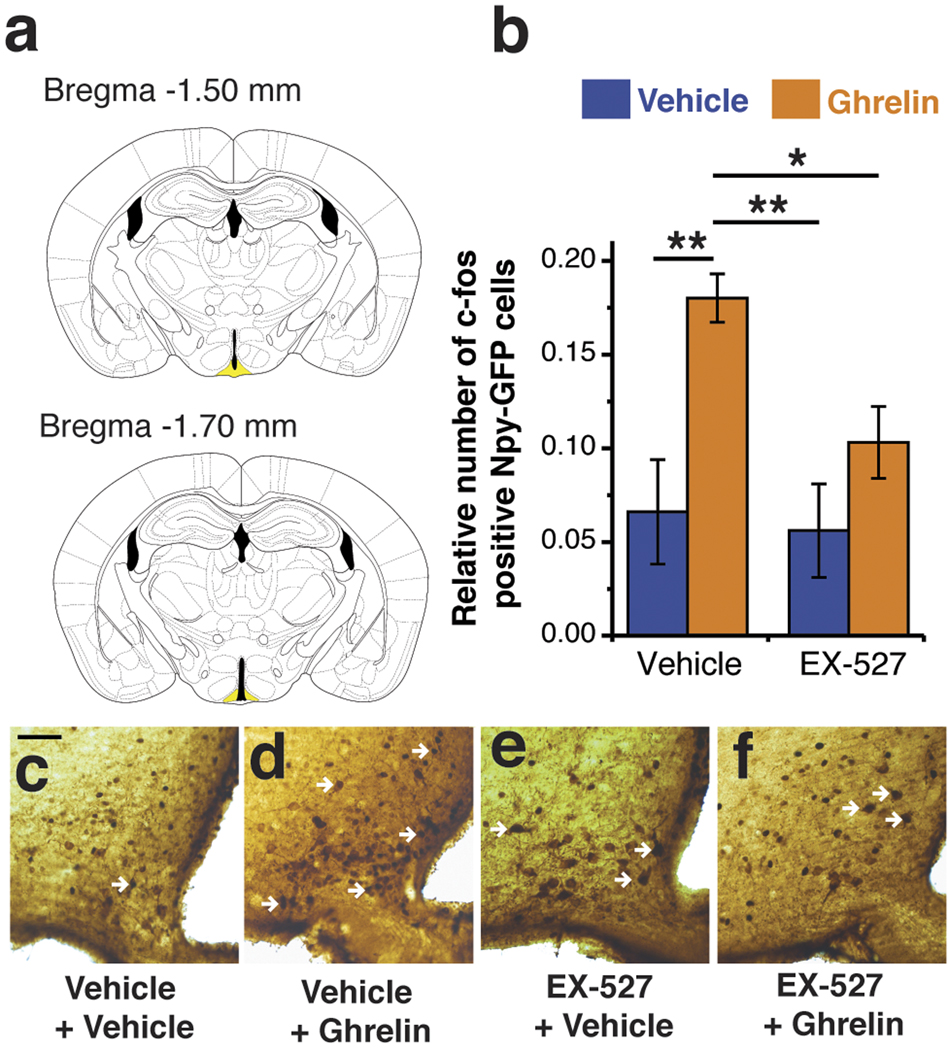
Figure 1. Sirt1 inhibition decreases ghrelin-induced c-fos expression in NPY/Agrp neurons.
EX-527 (i.c.v., 1.5 nmol/mouse), a pharmacological inhibitor of Sirt1 (Napper et al., 2005; Pacholec et al., 2010), diminished the number of c-fos labeled NPY-GFP cells after ghrelin treatment (i.p.). (a) slices from the brain highlighting the arcuate nucleus (ARC; in yellow) where the NPY-GFP and c-fos cells were counted (between bregma −1.50 mm to −1.70 mm). (b) Histogram showing quantification of double labeled NPY-GFP/c-fos cells in the ARC of mice injected with vehicle/EX-527 and vehicle/ghrelin. (c–e) Representative pictures of double immunohistochemistry for GFP (DAB - brown) and c-fos (Nickel DAB – black). White arrows indicate double stained cells. n = 4–5 mice/group. * p <0.05, ** p < 0.01.