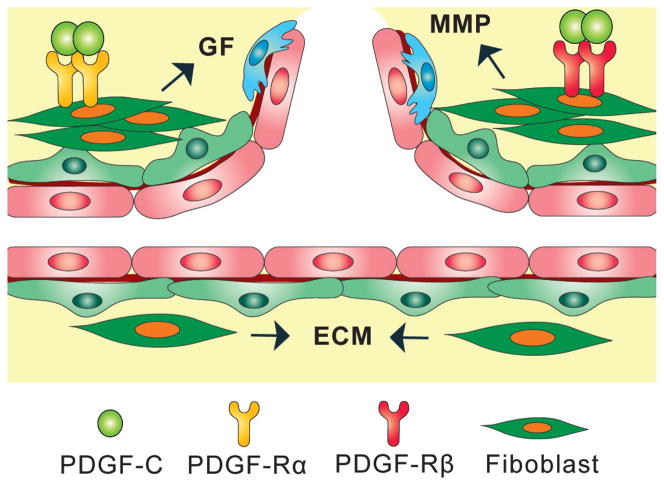
Figure 2. Effect of PDGF-C on fibroblasts.
Fibroblasts are the principal component of mesenchymal cells and are a major source of host-derived angiogenic growth factors (GF), extracellular matrix (ECM), and ECM-degrading proteases, such as the matrix metalloproteinases (MMP). Under pathological conditions, the number of fibroblasts is increased due to the upregulated expression of chemotactant and mitogenic factors. PDGF-C is one of the most potent stimuli of fibroblast proliferation, migration and recruitment. Part of the angiogenic activity of PDGF-C is therefore exerted via its effect on fibroblasts.