Figure 1. Protein blot showing light-dependent movement of Dmoesin from the membrane to the cytosol.
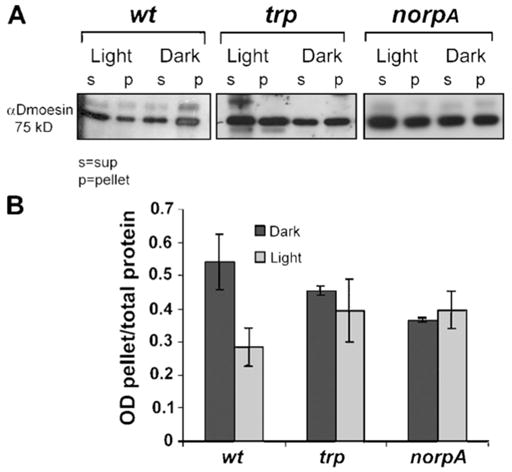
(A) Membrane-associated (pellet) and soluble (sup) protein fractions were separated by high-speed centrifugation and processed for Western blotting with αDmoesin antibodies. Head extracts were prepared from dark-raised (Dark) or illuminated (Light) flies of the following genotypes: WT, trpP343 (trp), and norpAP24 (norpA). Although illumination induces redistribution of Dmoesin from membranes to the cytosol in WT flies, inactivation of either TRP or NORPA blocks the light-dependent movement of Dmoesin. (B) The histogram plots Dmoesin levels in the pellet divided by the total amount of Dmoesin present in extracts from WT, trp, and norpA heads, as revealed from repeated experiments done in similar conditions to those in A. P < 0.01; n = 5. The error bars are SEM.
