Figure 6. Light- and phosphorylation-dependent interactions between Dmoesin and the TRP channel.
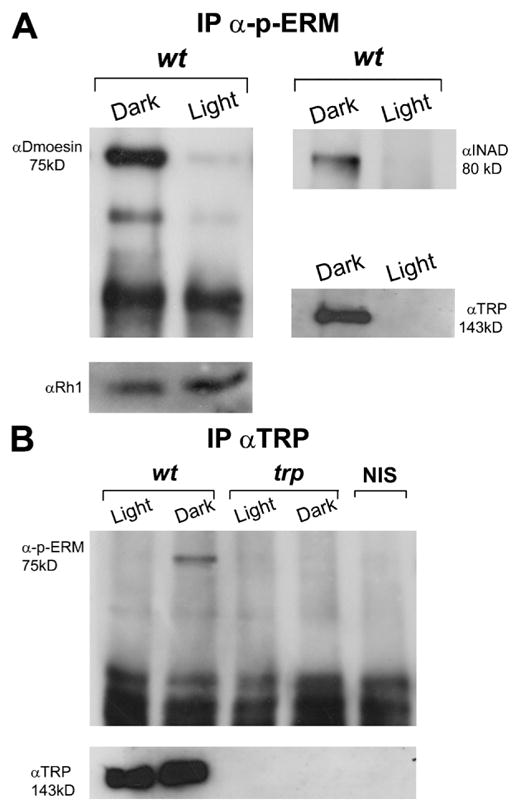
(A) Immunoprecipitation of D. melanogaster head extracts using α-phospho-ERM. Extracts were prepared from fly heads of dark-raised and illuminated WT flies and protein complexes were probed with αDmoesin (left) and with αINAD or αTRP (right) in a separate experiment. (bottom) Western blot analysis of the same head extracts probed with the major rhodopsin, αRh1. To detect TRP and INAD proteins in the immune complex, a threefold larger amount of head extracts were used (n = 5). (B) The experiments in A were repeated exactly, except that αTRP was used for the immunoprecipitation from head extracts of WT and trpP343 mutant, and protein complexes were probed with α-phospho-ERM. (bottom) Western blot of the same head extracts probed with αTRP. The two right lanes are Western blots from WT and trpP343 head extract probed with α-phospho-ERM (n = 4).
