Figure 1. Major Cellular Interactions and Regulatory Pathways Involved in IgA Responses to Intestinal Antigens.
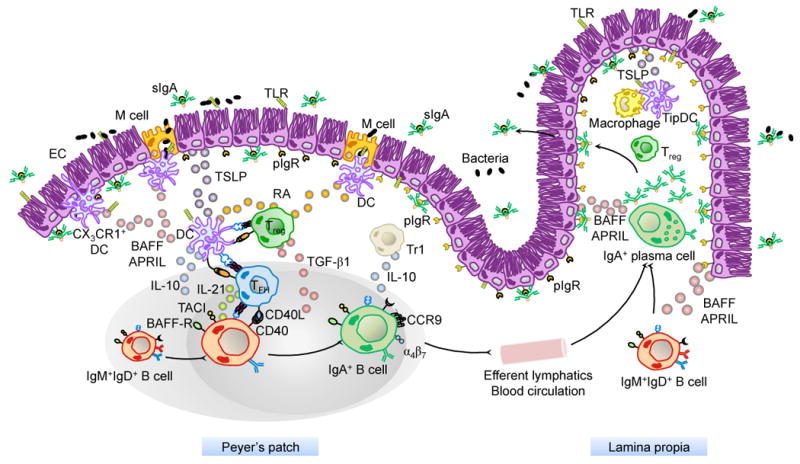
M cells from PPs sample commensal and vaccine antigens from the intestinal lumen and deliver them to subepithelial DCs. Antigen sampling is also carried out by CX3CR1+ DCs that project dendrites into the intestinal lumen across ECs. These cells release immunoregulatory (TSLP) and IgA-inducing (BAFF and APRIL) molecules upon sensing microbial signatures through TLRs and NLRs. TSLP stimulates the formation of tolerogenic DCs that suppress pro-inflammatory TH1 responses and induce non-inflammatory Treg responses by releasing IL-6, IL-10, TGF-β1 and RA. Treg cells may further differentiate into TFH cells, which together with Treg cells stimulate IgA CSR and production by stimulating naïve IgM+IgD+ B cells through CD40L, TGF-β1 and IL-21. In the presence of RA, IgA-expressing B cells emerging from mucosal germinal centers acquire expression of gut-homing receptors such as CCR9 and α4β7, which direct subsequent B cell migration to the intestinal LP through efferent lymphatics, regional mesenteric lymph nodes and blood circulation. In the LP, IgA-expressing B cells differentiate into IgA-secreting plasma cells that secrete IgA dimers. Interaction of IgA dimers with the pIgR results into IgA transcytosis and formation of a secretory IgA (SIgA) complex that binds antigen in the intestinal lumen. The LP also contains IL-10-producing macrophages and BAFF/APRIL/nitric oxide-producing TipDCs whose development is promoted by microbial and epithelial factors such as TSLP. TipDcs and macrophages would enhance local IgA production by triggering CSR and stimulating plasma cell survival.
