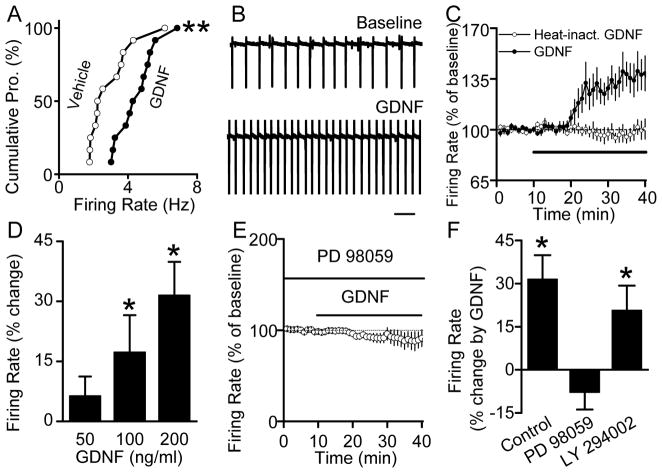
Figure 3. GDNF in the VTA increases the spontaneous firing rate of DA neurons in a MAPK-dependent manner.
A, Intra-VTA infusion of GDNF produces an increase in the spontaneous firing rate of VTA neurons. GDNF (10 μg/μl) or vehicle was bilaterally infused into the VTA, and slices were prepared 10 min later. Cumulative probability plot was constructed to compare the firing rates of individual neurons in slices from vehicle- and GDNF-treated rats. ** p < 0.01 vs. vehicle by Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, n = 12 cells from 3 rats for each group. B–D, Bath-applied GDNF increases the spontaneous firing frequency of DA neurons. B, Sample traces of spontaneous firing in a tight-seal cell-attached recording before (Baseline) and during (14 min) bath application of GDNF (200 ng/ml). Scale bar, 0.5 sec. C, Averaged time course showing that bath application of GDNF (200 ng/ml, black circles) (n = 14), but not its heat-inactivated form (heat-inact, GDNF, 200 ng/ml, white circles) (n = 8), induced an increase in the firing frequency of neurons. The horizontal bar depicts the application duration of GDNF or its inactivated form. For inactivation, GDNF was heated at 95°C for 1 hr. D, Dose-response of GDNF-induced enhancement of firing rate. * p < 0.05 vs. baseline. n = 10, 8, 15 for 50, 100, and 200 ng/ml GDNF, respectively. E–F, GDNF enhancement of the spontaneous firing rate of VTA neurons requires the activation of the MAPK pathway, but not the PI-3K pathway. Slices were pretreated with PD 98059 (10 μM), or LY 294002 (25 μM), for 45 min and GDNF’s (200 ng/ml) effect on the firing rate was tested in the continuous presence of the inhibitors. E, Firing rate of neurons in the presence of PD 98059 before and during GDNF application. F, Bar graph summarizing the effect of PD 98059 and LY 294002 on the firing rate of neurons in response to GDNF. * p < 0.05 vs. baseline. n = 9 (PD 98059), n = 11 (LY 294002). p = 0.15 for the difference in firing rate before and during GDNF application in the continuous presence of PD 98059. See also Figure S3.