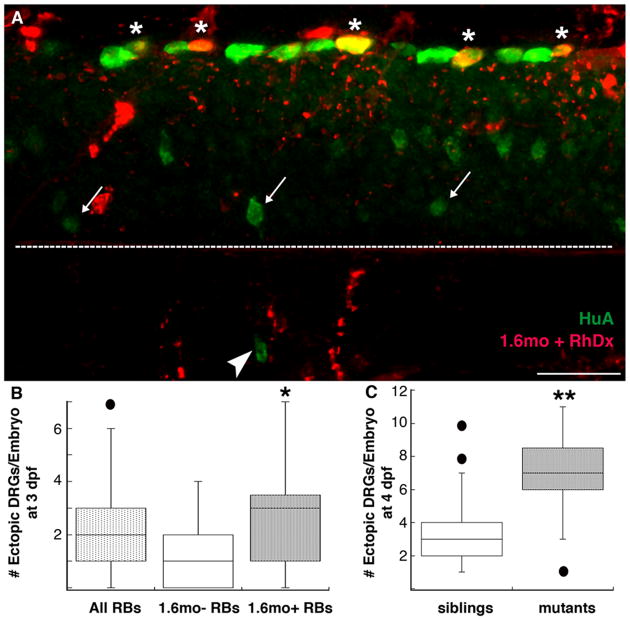
Figure 3.
Maintenance of DRG position/identity requires nav1.6a in RB cells. A,B, Ectopic DRG neurons (arrowhead), identified by HuA immunoreactivity (green), were present in mosaic embryos that contained RB cells (asterisks) with 1.6mo+ RB cells (red; yellow when co-present with HuA green signal). Arrows denote normally-positioned DRG neurons; the dashed white line indicates the spinal cord-notochord boundary. B, The number of ectopic DRG neurons increased in mosaic embryos that contained 1.6mo in RB cells compared to mosaic embryos that did not contain 1.6mo in RB cells (*p=0.02, Mann-Whitney U-test; n=44 embryos containing 1.6mo in RB cells, 22 embryos not containing 1.6mo in RB cells). C, mao mutants, characterized by reduced sodium current densities in RB cells (Ribera and Nüsslein-Volhard, 1998), have an increased number of ectopic DRG neurons versus sibling control embryos at 4 dpf (**p<0.0001 versus mao siblings, Mann-Whitney U-test; n=43 mao mutant and 99 sibling embryos). Scale bar, 25 μm.