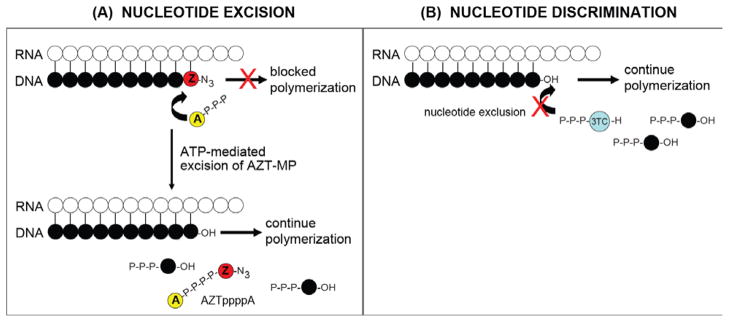
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of NRTI resistance. (A) Nucleotide excision. Mutations in pol, such as TAMs, aid in the ATP-mediated removal of an incorporated AZT monophosphate (AZT-MP) yielding an AZTppppA excision byproduct. (B) Nucleotide discrimination. Mutations in pol cause steric hindrance at the pol active site, excluding certain drugs, for example 3TC, from being incorporated during reverse transcription. Both examples yield a complex competent for polymerization. Yellow circle with the letter A and three phosphates, ATP; black circles with three phosphates, dNTPs; red circle with the letter Z and the N3 azido group, AZT-MP; blue circle with three phosphates, 3TC-triphosphate; P, phosphategroup. RNA is depicted with white circles; DNA is depicted with black circles.