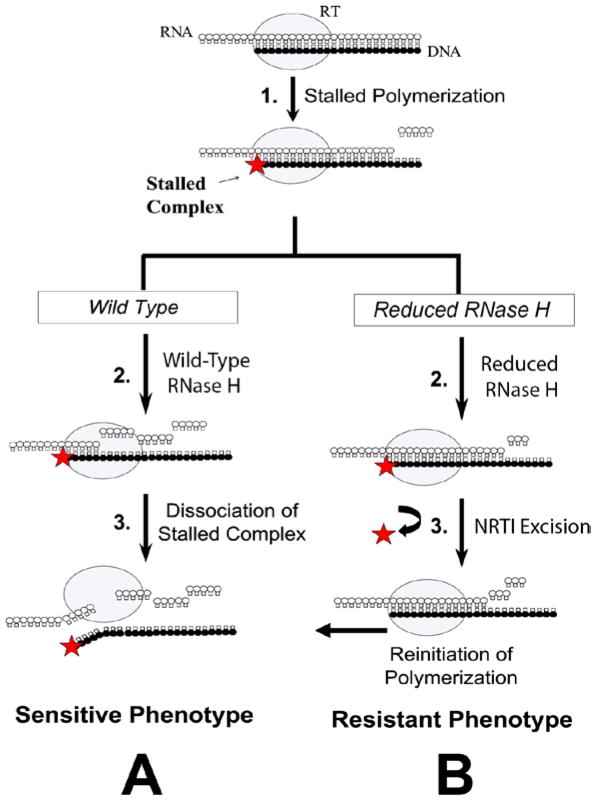
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of C-terminal domain NRTI resistance. During reverse transcription, incorporation of AZT leads to a complex stalled for polymerization. (A) In the case of a wild-type RT with wild-type RNase H activity, the stalled complex leads to a dissociation of the complex and sensitive phenotype as RNase H cleavage causes minimal stretches of homology to be retained between the RNA/DNA hybrid. (B) In the case of an RT with reduced RNase H activity, the decrease in template RNase H cleavage allows longer stretches of homology to be retained between the RNA/DNA hybrid giving more time for the pol active site to undergo nucleotide excision and reinitiate polymerization, leading to a resistant phenotype. Gray oval, reverse transcriptase; star, AZT; white circles, RNA; black circles, DNA.