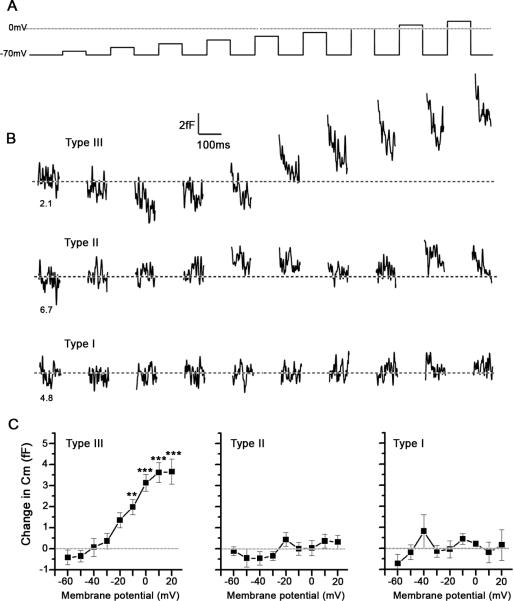
Figure 3. Type III, but not Type II and Type I taste cells exhibit voltage-induced increases in membrane capacitance (Cm).
(A) The sequence of voltage pulses, in 10 mV increments, applied to the taste cells clamped at -70 mV. (B) Representative depolarization-induced changes in Cm (100 Hz, low pass, Gaussian filter) in Type III, Type II and Type I taste cells. The numbers beneath each trace represent the resting Cm of each taste cell. (C) Average depolarization-induced changes in Cm in Type III, Type II and Type I cells, recorded in 18, 12 and 10 cells, respectively. Error bars represent SEM. The asterisks represent the significance level compared to the Cm at the first voltage step (*** P<0.001; ** P<0.01; one way ANOVA with Tukey's Multiple Comparison Test).