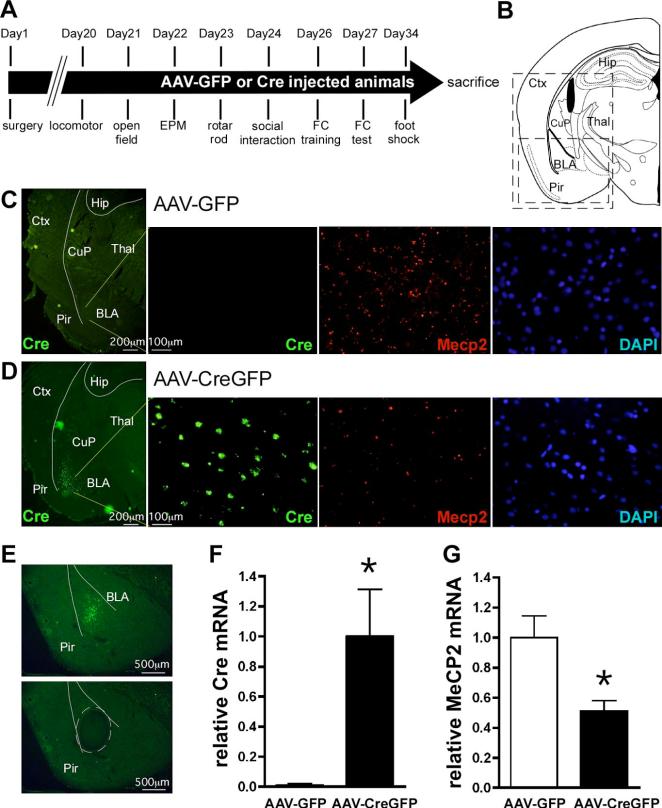
Figure 1.
AAV-CreGFP-mediated deletion of Mecp2 from BLA neurons. A, Experimental timeline for the behavioral experiments. B, A schematic of a mouse brain coronal section at −1.94 mm relative to bregma (adapted from Paxinos and Franklin (2001). The large box indicates the regions shown in C and D, whereas the small box represents the region shown in E. C,D, Double labeling fluorescent in situ hybridization of Cre recombinase and Mecp2 expression, visualized by FITC and Cy3 epifluorescence, respectively, in mice bilaterally injected into BLA with AAV-GFP (C) or AAV-CreGFP (D). From left, detection of Cre recombinase mRNA in the left side of a coronal section with low magnification, Cre recombinase expression, Mecp2 expression, and DAPI staining within BLA of the same field with high magnification.E, BLA containing GFP epifluorescence was laser microdissected out and subjected to real-time PCR for quantitation of Cre recombinase and Mecp2 mRNA levels. Presented is an example of the coronal section before (top) and after (bottom) laser microdissection. A microdissected region was traced with broken lines. F,G, QRT-PCR analysis of Cre recombinase (F) and Mecp2 (G) expression from laser-captured BLA. The data were normalized to 18S rRNA. *p < 0.05 by Student's t test; AAV-GFP, n = 13; AAV-CreGFP, n = 10. Ctx, Cortex; Hip, hippocampus; CuP, caudate putaman; Thal, thalamus; Pir, piriform cortex.