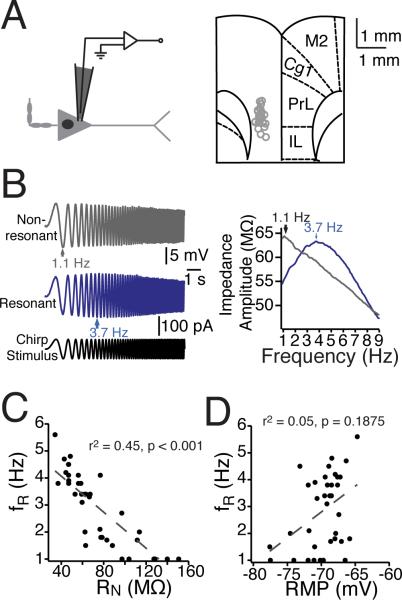
Figure 1. Heterogeneity in mPFC neurons’ dynamic properties.
(A) Somatic recordings of layer V mPFC neurons were conducted within ventral mPFC, including prelimbic and infralimbic cortex. Left panel: a schematic of a mPFC neuron and the somatic recording location. Right panel: Recording locations overlaid with a modified version of a coronal diagram from the Rat Brain Atlas (Paxinos & Watson 1993). (B) In response to a 10-s Chirp stimulus at their resting membrane potential, different mPFC neurons resonated across a range of (1-6 Hz) of frequencies. In addition to exhibiting different resonance profiles, neurons were diverse in both ( C) steady-state input resistance.and (D) resting membrane potential n = 38 neurons. Gray dashed lines represent the linear fit of the data, with correlation values listed. Abbreviations: PL, prelimbic, IL, infralimbic, Cg1, anterior cingulate, and M2 secondary motor cortices.