Figure 1. Biological comparisons between MSC and MPC.
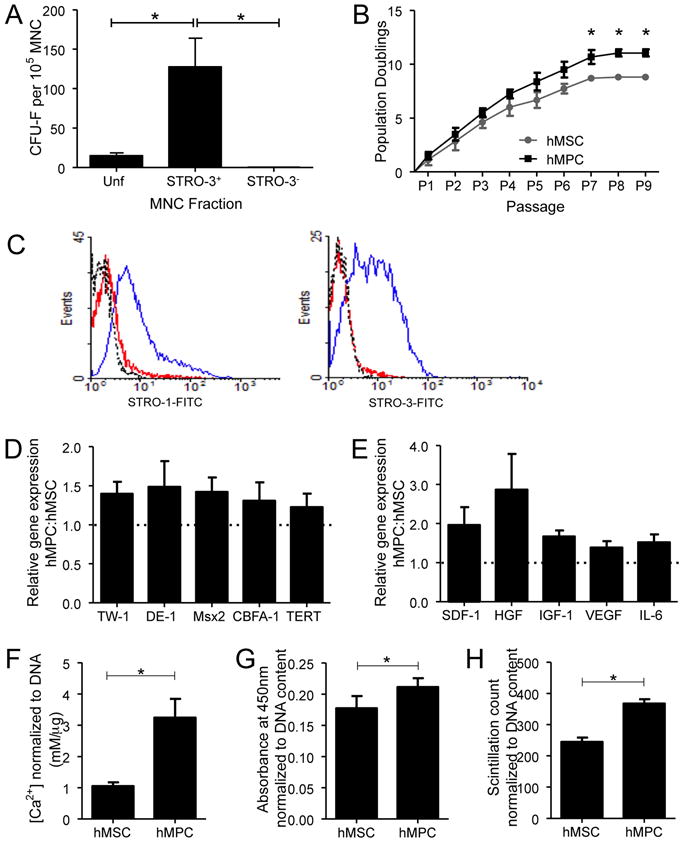
(A) The clonogenic efficiency of each MNC fraction. Results shown are the mean±SEM number of CFU-f per 105 cells plated for unfractionated (Unf), STRO-3+ and STRO-3-depleted (STRO-3-) MNC (*P<0.001, average of five donor experiments). (B) Mean number of population doublings (±SEM) of MSC and MPC during ex vivo culture from P0 to senescence. (*P<0.05, average of 3 donor experiments). (C) Examples of flow cytometric histograms comparing MPC and MSC from the same donor, for surface STRO-1 and STRO-3 expression at P4. Dotted line – isotype control. Red line - MSC. Blue line – MPC. P4 MPC gene expression of various immature “stem cell” markers (D) and cytokines (E). Results are presented as mean ratio±SEM of gene expression in MPC relative to MSC (average of three donor experiments). P4 MSC and MPC differentiation capacity for mineralization (F), adipogenesis (G) and glycosaminoglycan synthesis (H), under the respective in vitro inductive conditions. Data are presented as mean±SEM. (*P<0.05, average of 3 donor experiments.)
