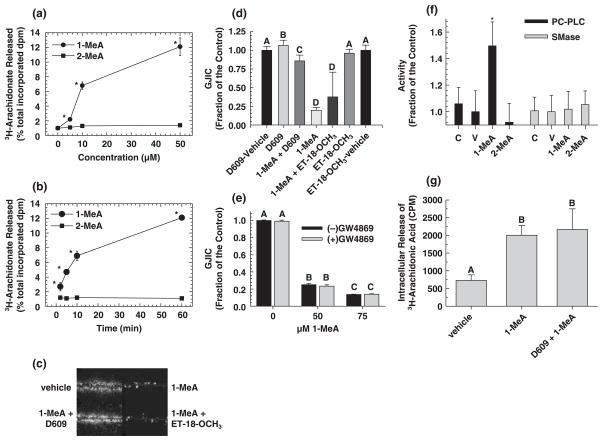
Fig. 2.
The role of phospholipid signaling in 1-methylanthracene (1-MeA) versus 2-methylanthracene (2-MeA) induced effects on gap junctional intercellular communication (GJIC). (a) The effect of 1-MeA versus 2-MeA doses on the release of arachidonic acid. (b) The effect of 1-MeA versus 2-MeA exposure times on the release of arachidonic acid. (a,b) 0.1% albumin was added to the medium to inhibit reacylation and metabolism of released 3[H]-arachidonic acid therefore the data reflected cumulative deacylation from membrane phospholipids. At the end of the incubation period, the medium was collected into scintillation cocktail solution and radioactivity determined by scintillation counting of disintegrations per minute (dpm). Radioactivity in the cellular fraction was also determined, and 3[H]-fatty acid release was expressed as a percentage of total cellular radioactivity. The data are an average of at least four independent treatments, and *indicated significant differences paired between 1-MeA and 2-MeA for each dose and time as determined by a two-tailed paired t-test at the 95% confidence interval, P < 0.001. (c) The effects of phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitors on 1-MeA-induced inhibition of GJIC. The scrape load-dye transfer (SL-DT) assay was used to assess GJIC at 200×. (d) Presents a summary of the averaged data of n = 3, including those shown in (c). (c,d), Phosphatidylcholine(PC)- and phosphatidylinositol(PI)-specific-PLC were inhibited by preincubating the cells for 15 min with either 50 μM D609 or 30 μM ET-18-OCH3, respectively. The inhibitors were left on the cells for an additional 15 min, which was the exposure time of 1-MeA. The dose of 1-MeA was 70 μM. The data are an average of the data (n = 3) ± standard deviation at the 95% confidence level. An ANOVA indicated significance at P < 0.001, F = 420.1, and the different letters (A, B, C and D) indicated significance using an all pair multiple comparison-Holm Sidak posthoc T-test at the P = 0.05 level. (e) The effect of a sphingomyelinase inhibitor on 1-MeA-induced inhibition of GJIC. The SL-DT assay was used to determine GJIC. The incubation time of 1-MeA was 15 min, and the concentration and preincubation time of the sphingomyelinase inhibitor, GW4869 (N,N′-Bis[4-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)phenyl]-3,3′-p-phenylene-bis-acrylamide dihydrochloride) was 40 μM and 30 min. The results are an average of the data (n = 3) ±standard deviation at the 95% confidence level. An ANOVA indicated significance at P < 0.001, F = 3743.6, and the different letters (A, B and C) indicated significance using an all pair multiple comparison-Holm Sidak posthoc T-test at the P = 0.05 level. (f) The effects of 1-MeA versus 2-MeA on the activation of either PC-PLC or sphingomyelinase (SMase). An AmplexRed assay system as described in the methods and material section was used to measure the activities of the indicated lipases. The concentration and incubation times of the PAH were 100 μM and 15 min. The results are an average of the data (n = 5) ±standard deviation at the 95% confidence level. An ANOVA indicated significance at P = 0.003, F = 5.153, and the *indicated significance from all other groups using an all pair multiple comparison-Holm Sidak posthoc T-test at the P = 0.05 level. (g) Intracellular release of 3[H]-arachidonic acid from cells treated with 1-MeA and a phosphatidylcholine-specific PLC inhibitor. The extracellular media was decanted, cells rinsed with phosphate buffered saline and then 1 mL of 0.5% bovine serum albumin in water was added to the cells for 10 min to extract the intracellular arachidonic acid and the radioactivity was determined by scintillation counting of counts per minute (CPM). The results are an average of the data (n = 3) ± standard deviation at the 95% confidence level. An ANOVA indicated significance at P < 0.001, F = 25.2, and the different letters indicated significance using an all pair multiple comparison-Holm Sidak posthoc T-test at the P = 0.05 level.