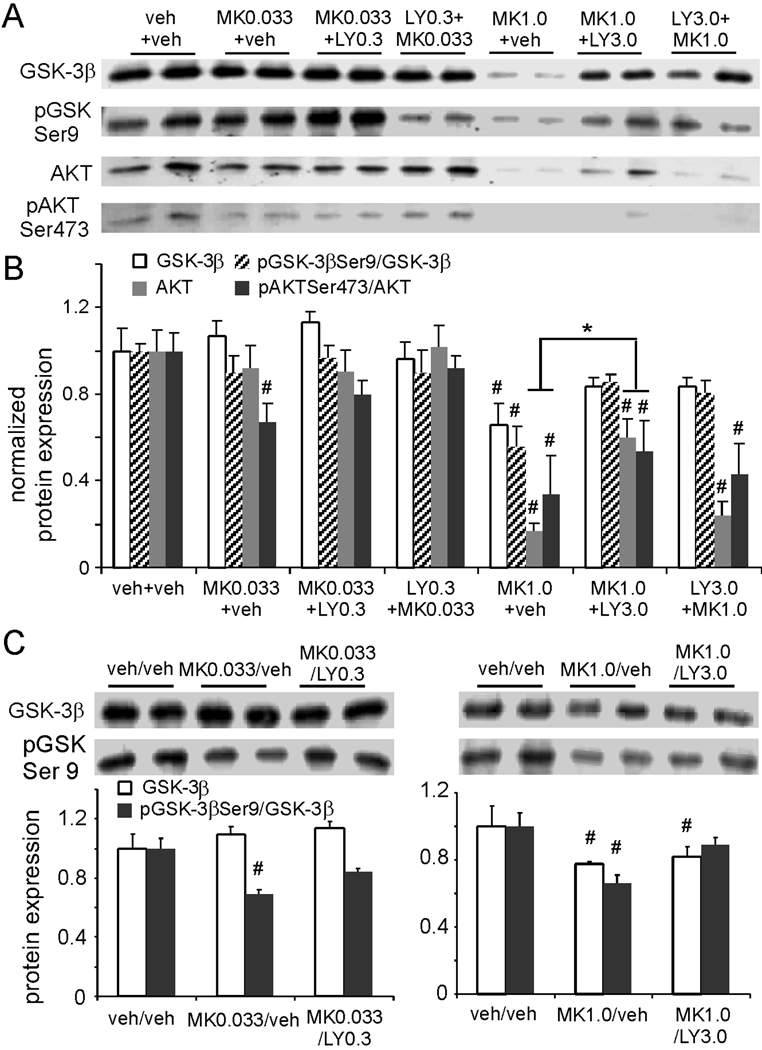
Figure 7.
Activation of the Akt/GSK pathway contributes to the postsynaptic effects of the mGluR2/3 agonists. (A and B) Immunoblots and summary histogram show the expressions of GSK-3β, pGSK3βSer9, Akt, and pAktSer473 in control and six acute treated groups. Acute MK-801 at low-dose (0.033 mg/kg) induced negligible effects on total protein levels of GSK-3β and (P > 0.05) and of pGSK-3β Ser9 level (P > 0.05), but a significant decrease of pAkt Ser473 (P < 0.05), indicating a possible increase of GSK-3β activity. LY379268 rescued the ratio of pAkt Ser473/Akt to vehicle control levels. In contrast, high-dose MK-801 (1 mg/kg) significantly decreased the total proteins of GSK-3β and Akt (P < 0.05), as well as the ratios of pGSK-3β Ser9/GSK-3β and pAkt Ser473/Akt (P < 0.05). LY379268 treatment partially but significantly reversed the alterations of Akt and pAkt Ser473/Akt (P < 0.05) when it was applied after but not prior to MK-801 administration. The expressions of GSK-3β and pGSK-3β Ser9/GSK-3β were, however, similarly recovered by treatment with LY379268. (C) Subchronic MK-801 at 0.033 mg/kg significantly decreased pGSK Ser9 (P < 0.05), but not total protein of GSK-3β (P > 0.05), and this decrease was reversed by LY379268 at 0.3 mg/kg (P > 0.05). In contrast, both GSK-3β and pGSK Ser9 were significantly decreased by subchronic MK-801 at 1.0 mg/kg (P < 0.05), and LY379268 at 3.0 mg/kg restored pGSK-3βSer9 levels (P > 0.05) but had minimal effects on total GSK-3β expression (P < 0.05).