Figure 1.
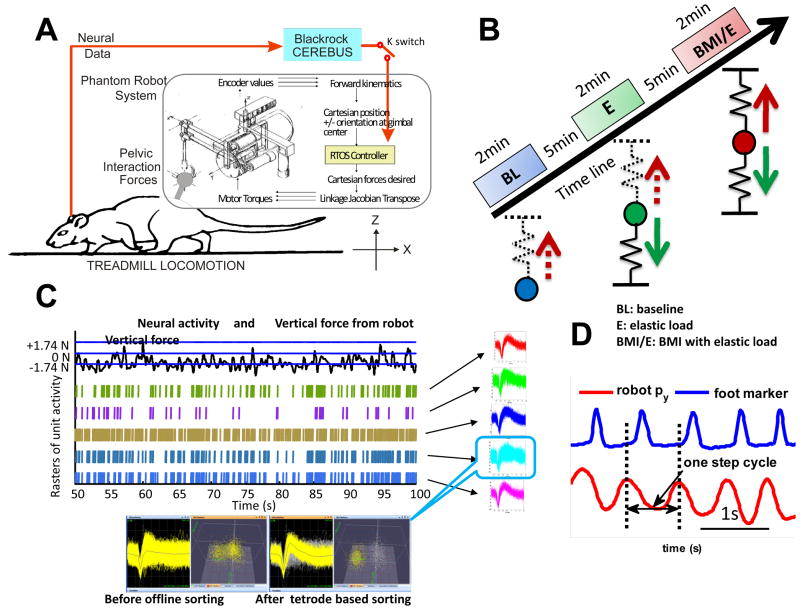
Experimental setup and training protocol. A. Rats were trained to walk on a treadmill with robot attached to the pelvis through a pelvic implanted orthosis, and neural activities were recorded from the motor cortex of the hindlimb/trunk area. The BMI could be engaged or disengaged (‘switch K’) while a simple elastic load was applied to a rat. RTOS – real-time operating system of robot. Blackrock Cerebus – neural acquisition system. B. Training sessions were composed of three trials with2min baseline (BL), 2min simple elastic load (E) trial and 2min BMI with elastic load trial (BMI/E) with 5–10min resting time between trials. The elastic load on the rat and the interaction force differed in each case: in baseline there was no force, but kinematics of the pelvis were collected with the robot; in simple elastic load trials interaction force was an elastic load (solid downward green arrow) and there was no BMI effect; in BMI with elastic load trials interaction force was the sum of the simple elastic load (green arrow) and a neural driven BMI elastic force (solid red arrow). The neural driven force in the control was calculated from the aggregate firing rate in a 100ms window which modulated the stiffness of a lifting elastic field (solid red arrow) in BMI with elastic load condition. The instantaneous ‘virtual neural driven force’ in baseline and simple elastic load could be calculated offline from neural firing and kinematics (upward dotted red arrows). C. Individual neurons were detected based on the waveforms of the spikes and used in the BMI. The online detected spikes from 5 channels are shown before offline sorting. One unit is shown before and after offline sorted is shown below with the scatter plot of the first 2 tetrode principle components. Neural firing was recorded and could be correlated to kinematics or interaction forces when the rats adapted in different conditions. D, The Step cycle was identified from robot tip motion Py position (red), collected at 1KHz, which corresponds to the pelvis lateral motion or step width, and this measure correlated well to video tracking as checked by toe marker from our video tracking system (blue).