Fig. 2.
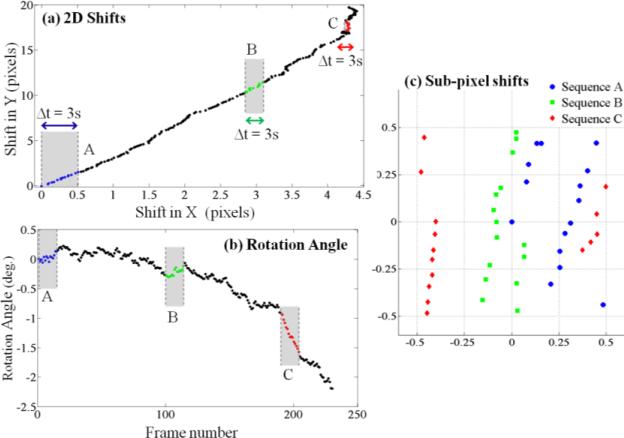
Electro-kinetic motion: As the object flows through the micro-channel due to electro-kinetic motion, lensfree in-line holograms are continuously captured by the CMOS sensor at a rate of ~5-6 frames/sec. Acquisition of ~15 consecutive frames is sufficient to generate a high-resolution HOM image, but for image comparison purposes, 230 frames were captured during ~45 seconds. (a) The two-dimensional lateral shifts of consecutive frames with respect to the first one. (b) In-plane rotation angles of consecutive frames with respect to the first one. (c) Sub-pixel shifts of 3 sequences (A, B and C), each composed of 15 consecutive frames are shown. These 3 sequences of lensfree raw holograms are used independently to generate 3 different HOM images. Integer pixel shifts are not useful for the super-resolution algorithm and are therefore digitally subtracted out.