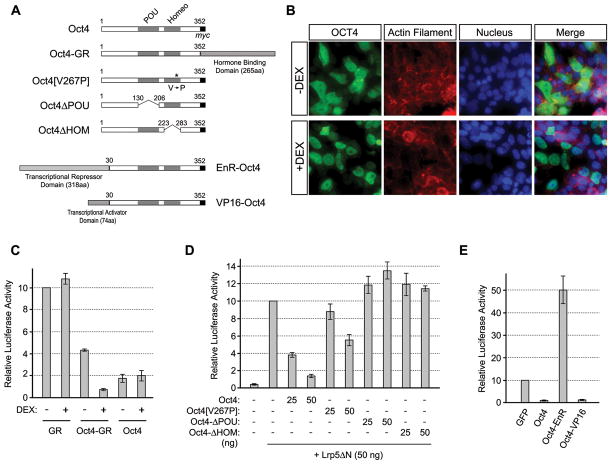
Figure 4.
Nuclear function of Oct4 is critical for suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. (A) Structures of various modified Oct4 constructs. (B) Distribution of Oct4-GR fusion protein in response to dexamethasone (DEX) treatment (1 μM). The fusion protein is detected immunocytochemically using anti-Oct4 antibody. Actin filament and nucleus are visualized with Alexa 546-phalloidin and DAPI, respectively. (C) Effective inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by Oct4-GR in the presence of DEX. (D) Effects of Oct4 deletion and mutation constructs on Wnt/β-catenin signaling. (E) Effects of EnR-Oct4 and VP16-Oct4 on Wnt/β-catenin signaling. In (B–E), cells are fixed for immunostaining or lysed for luciferase assay one day after plasmid transfection.