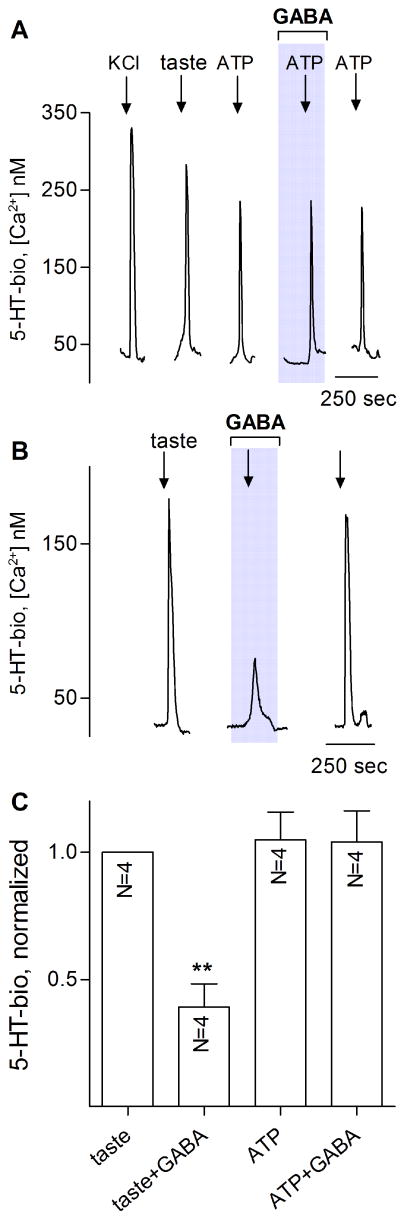
Figure 4. In isolated taste buds, GABA interrupts communication between Receptor cells and Presynaptic cells.
Isolated taste bud were sequentially depolarized with KCl, stimulated with tastants and with ATP, in the absence or presence of 10 μM GABA. A, Traces show stimulus-evoked 5-HT release from Presynaptic cells within the taste bud (i.e., responses from a 5-HT biosensor apposed to the taste bud). All stimuli (arrows) elicit 5-HT release as shown previously (Huang et al., 2007). GABA has no effect on ATP-evoked 5-HT release. B, same taste bud, showing effects of GABA on taste-evoked 5-HT release. Here, Presynaptic cells are indirectly triggered to release 5-HT and GABA-mediated inhibition is consistent with GABA acting to reduce ATP release from Receptor cells, thereby interfering with cell-cell excitation of Presynaptic cells. C, summary of several experiments as those in A,B. Details of bars and analyses as in Figure 1.