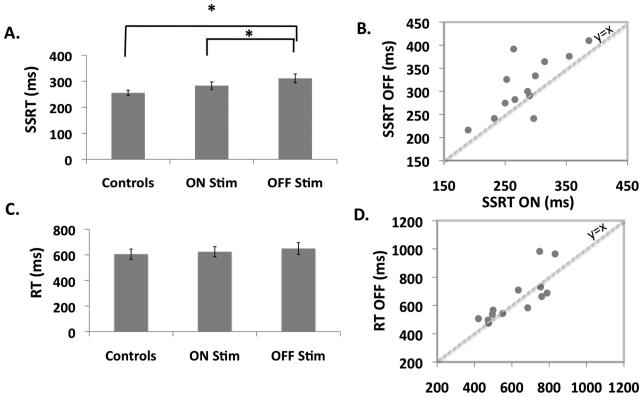
Figure 2. Behavioral Results.
A. Stop Signal Reaction Times (SSRTs) was significantly longer for patients OFF stimulation compared to ON stimulation and for patients OFF stimulation compared to controls (both p<0.05). B. SSRTs for individual patients. SSRT estimation was reliable since there was a strong correlation (r = 0.74, p<0.01). The speeding of SSRT for ON versus OFF stimulation was also robust since every patient bar one improves. C. Go RT was not different. D. Go RT for individual patients. There was a strong correlation between ON and OFF (r = .81, p<0.01), however STN DBS did not affect Go RT consistently.