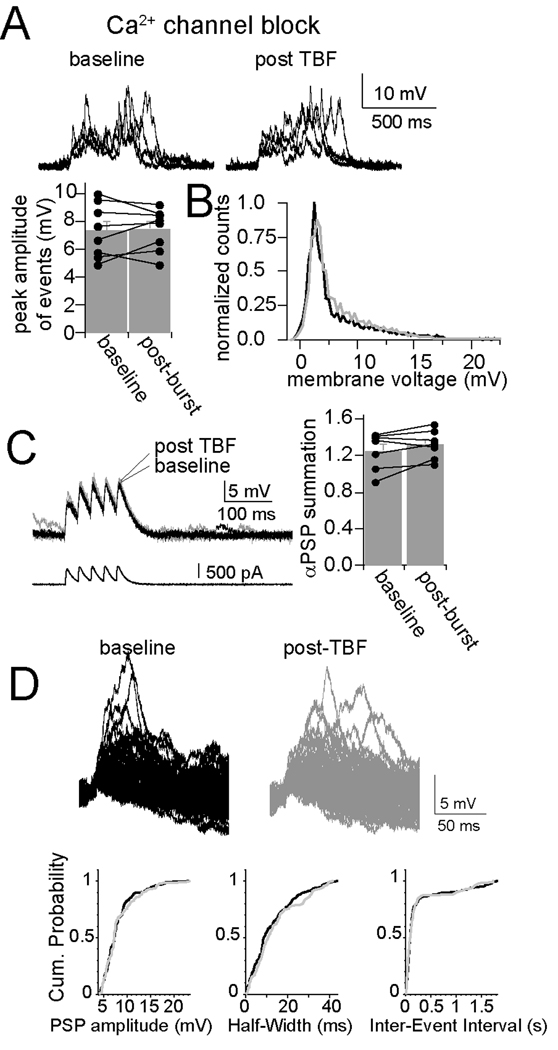
Figure 7. Plasticity of synaptic integration is dependent upon calcium channels.
A) Blockade of Ca2+ channels with intracellular Cd2+ (depicted here) or Ni2+ blocks the effects of TBF on integration of spontaneous synaptic events, demonstrated by the absence of a change in the average peak amplitude of bursts of synaptic events, and B) by absence of a shift in the distribution of the membrane potential (black line is baseline, grey line is post-TBF). C) Consistent with this, the effect of TBF on summation of αPSPs was blocked by intracellular blockade of Ca2+ channels (Cd2+ depicted here). D) Modification of spontaneous single synaptic events was also absent after TBF when intracellular blockers of Ca2+ channels were present (in this case Cd2+); neither the amplitude, half-widt, nor inter-event interval (h) was modified by theta burst firing.