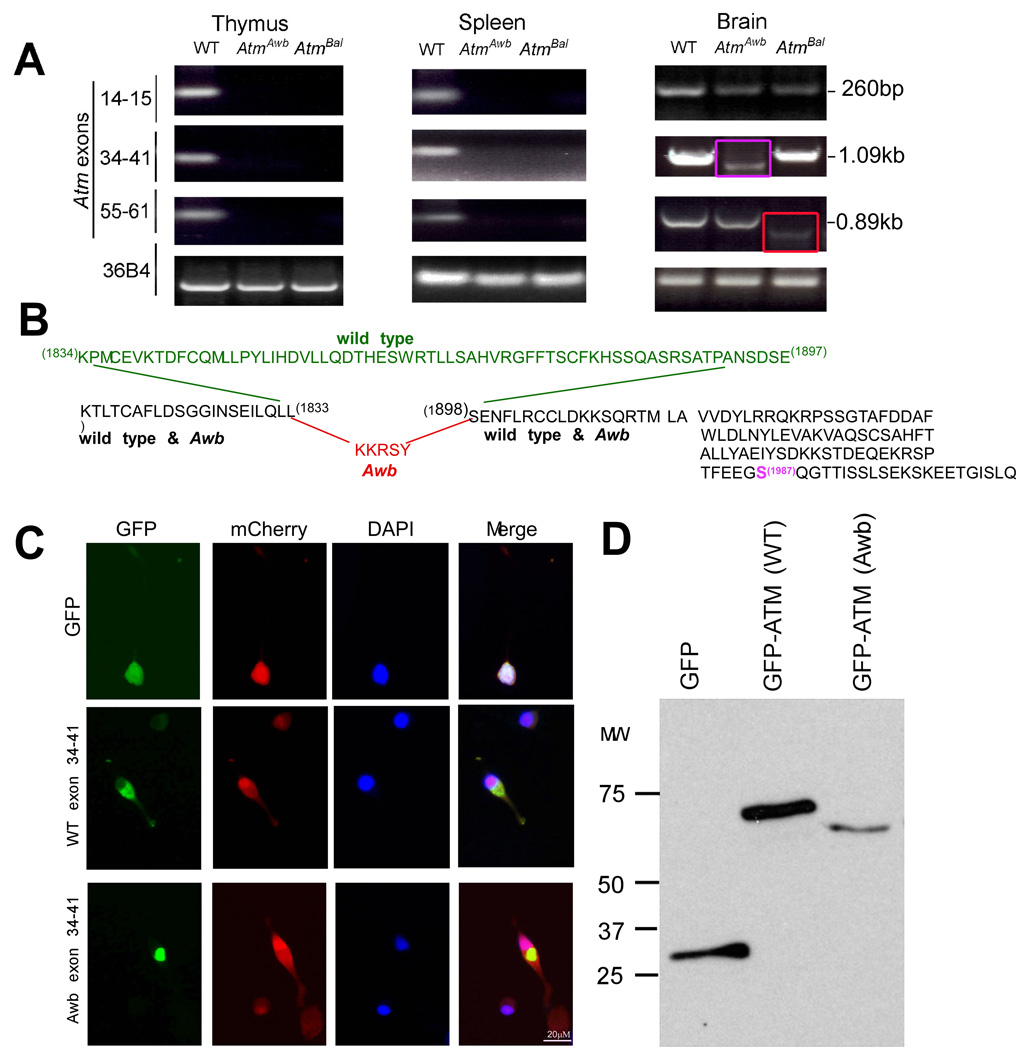
Figure 4. Brain-specific Atm mRNA found in both Atmtm1Awb and Atmtm1Bal mice.
A) RT-PCR reveals alternative message forms in Atmtm1Awb and Atmtm1Bal mouse brain. RNA was extracted from wild type and Atmtm1Awb and Atmtm1Bal tissues as indicated, reverse transcribed and amplified by primers located in the exons indicated at the left. 36B4 mRNA was used as a control. The red arrow indicates that the brain Atmtm1Awb message is reduced in size, relative to wild type in the region between exons 34 and 41; the purple arrow indicates that the Atmtm1Bal message is also reduced in size, relative to wild type in the region between exons 55 and 61.
B) Based on DNA sequencing, the predicted protein sequence of the RT-PCR products is shown. The portion of the wild type message that is deleted in the Atmtm1Awb message is shown in green; the 5 amino acids added to the Atmtm1Awb message are shown in red. The grayed amino acid sequence to the right shows the common continuation of both mutant and wild type message through the codon for the autophosphorylated serine 1987 (magenta) and beyond.
C) Images of GFP fusions with short ATM peptides encoded by the PCR amplified product of exons 34 through 41 of mouse ATM cDNA. Wild type and Atmtm1Awb GFP-fusion peptides distribute primarily to the cytoplasm of transfected N2a cells (2nd and 3rd rows), compared with a GFP-only construct (top row). In each experiment mCherry was co-transfected to identify all transfected cells.
D) Western blots of cell lysates from N2a cells transfected with GFP, and the GFP fusion peptides described in C. Blots were probed with GFP antibody.