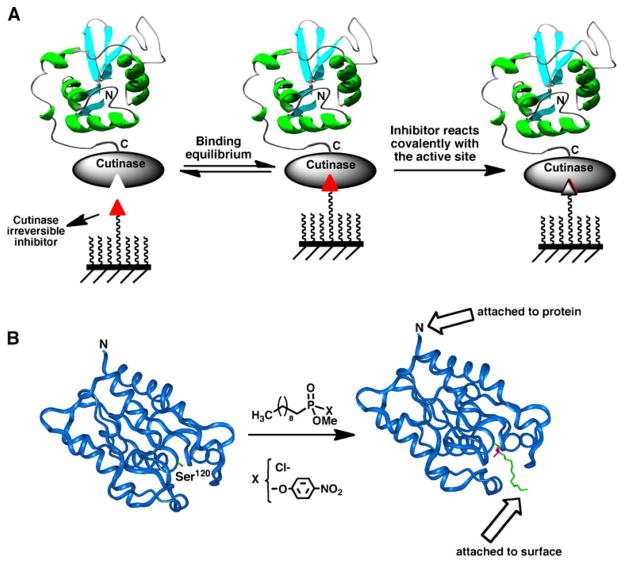
Fig. 5.
A Site-specific immobilization of cutinase-fusion proteins using an active site-directed capture ligand. B Structure of F. solani cutinase enzyme free and bound to the inhibitor n-undecyl-O-methyl phosphonate chloride. The inhibitor is covalently bound through the side-chain hydroxyl group of the Ser120 residue, which is located at the active site of the enzyme (113).